SOAR is a set of tools that help organizations and enterprises efficiently respond to cyberthreats by automating important tasks involved in robust cybersecurity practices.
The acronym SOAR stands for Security, Orchestration, Automation & Response.
SOAR tools help streamline security from multiple vendors in vulnerability management, incident response and security operations automations.
SOAR platforms give security teams a centralized point of operations where they can integrate multiple security tools into a well optimized threat response workflow. As part of this, low level repetitive tasks within these workflows can be automated, streamlining the full process.
Read: Top 10 Best SOAR Solutions for 2024
This centralized platform can also allow security teams to review all security notifications from individual tools in one place.

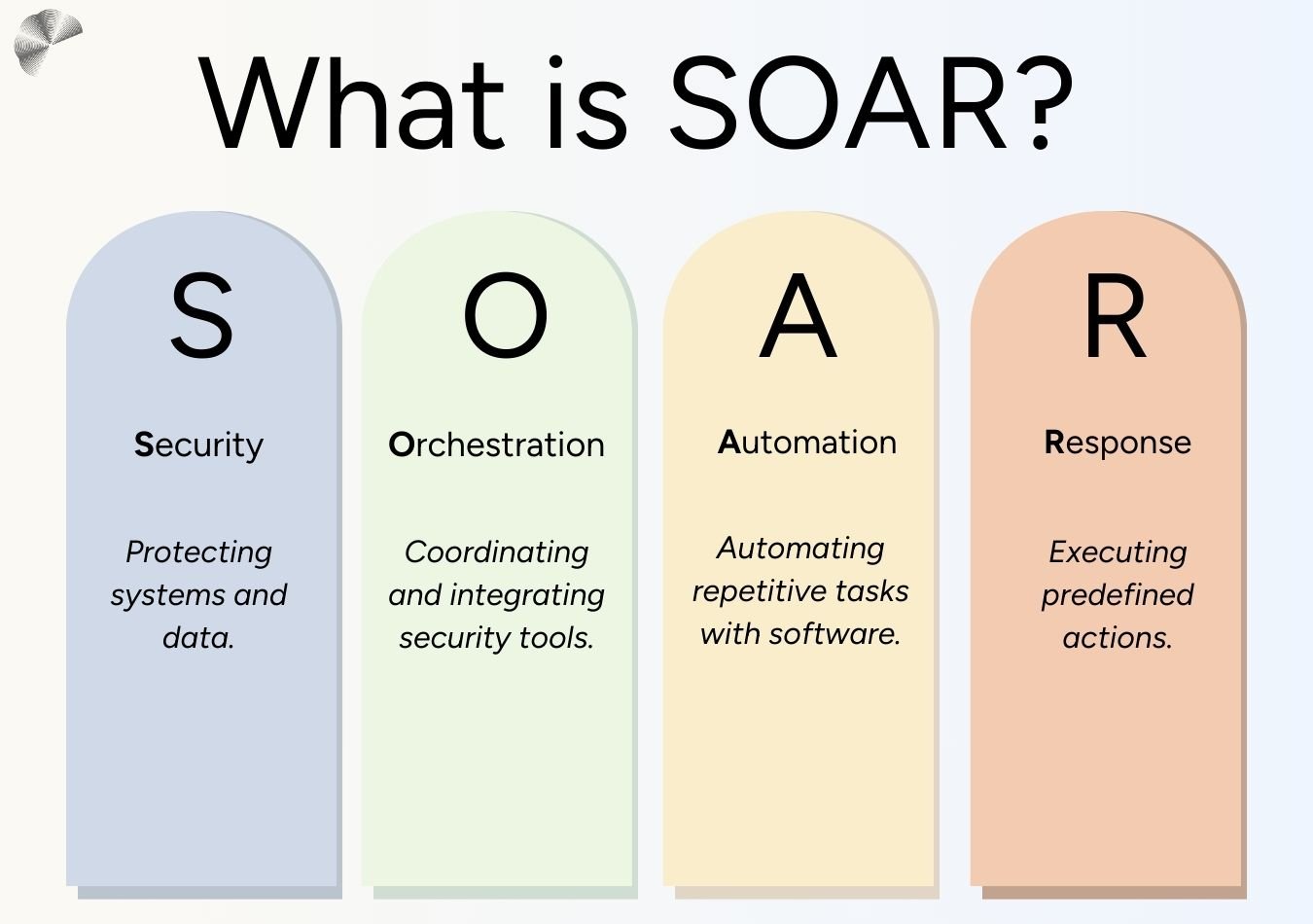
Orchestration in SOAR refers to the process of coordinating and managing multiple security tools and processes to work together seamlessly. This coordination is the basis for the centralized SOAR platform operating and ensures that different security tools can share information, trigger automated responses, and work together to protect an organization's systems.
Automation in SOAR refers to the process of using a software to tool perform repetitive tasks automatically, meaning it operates without a human intervening or overviewing. This can speed up security operations significance and substantially reduce human error.
Response in SOAR refers to the actions taken in the automated processes. When a security incident is detected, SOAR can automatically trigger a response. This could be blocking a malicious IP address, isolating a compromised system or alerting a security team. The ‘response’ can also refer to automating sending notifications to relevant stakeholders. By automating the response process SOAR can reduce the time it takes to contain and resolve a security incident.
How to SOAR Tools Work?
SOAR automates the data collection process from security tools like SIEM, vulnerability scanners, and threat intelligence feeds. These tools first analyze and then prioritize threats based on severity, potential impact, and context. This process helps security teams focus on the most critical threats first.
SOAR also allows for the creation of automated workflows for handling specific types of threats. This triggers specific actions including isolating infected devices, blocking malicious IPs, and escalating the incident to analysts.
SOAR can also provide comprehensive reports on each threat, allowing security teams to track progress and identify any additional vulnerabilities.
In the response phase the system will automate repetitive tasks. It prioritizes alerts based on severity, potential impact, and context. This ensures that response teams can focus on the most critical incidents first, reducing the Reduced Mean Time to Response (MTTR).
AI and SOAR
Many SOAR solutions now leverage AI and machine learning to analyze data and learn from past incidents.
Machine learning algorithms can analyze current and historical security data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential threats. AI can also monitor user behavior to detect any deviations from a user's typical patterns.
AI is also able to process and interpret threat intelligence updates to stay aware of the latest threats and potential vulnerabilities
AI can also be useful in the automation of the incident response. By dynamically adjusting incident response playbooks the AI can not only predict potential threats but proactively implement preventative measures.
SOAR is a powerful cybersecurity tool, able to bolster and automate key tasks at the enterprise level and beyond. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect advancements in SOAR solutions. AI-powered SOAR platforms will be capable of proactively identifying threats, automating complex tasks, and tailoring security measures to specific organizational needs.

When Buildings Run Themselves
How integrated BAS platforms turn HVAC, lighting, safety and access into a single control layer for leaner, data-driven facilities operations.
However, it's crucial to remember that as security capabilities improve, so too do the tactics employed by cybercriminals. They will likely develop more complex attacks to bypass advancing security measures as well as find and exploit vulnerabilities in new technologies.
To stay ahead of these evolving threats, organizations of all sizes must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity, continuously updating their defenses and staying informed about the latest threats.







Comments ( 0 )