Less than a year after the launch of Bard AI, Google has renamed the popular chatbot to the upgraded AI model that was powering it – Gemini.
The overhaul, which CEO Sundar Pichai believes represents “the beginning of a new era of AI,” gives users access to Google’s newest and “most capable” large language model (LLM) yet, along with a new look and a range of new features that make it a major upgrade from Bard.
Gemini has advanced "reasoning capabilities" according to the CEO, allowing it to "think more carefully" when answering difficult questions and reducing the risk of “hallucinations” that other AI models, including Google’s own, have struggled with.

The AI model comes in three versions, and is “multimodal”, which means it can understand text, audio, images, video and computer code simultaneously.
It has also been integrated into Google products including its search engine, and is being released initially in more than 170 countries as an upgrade to Bard.
US customers can subscribe for $19.99 a month to access Gemini Advanced, which includes Google’s most powerful Ultra 1.0 AI model, the company said.
Similar to OpenAI’s GPT-4, Gemini Ultra 1.0 is better at understanding the nuance and context of user prompts and performs better at jobs like writing code when compared to Bard and other previous models.
Read more: Gemini vs ChatGPT: Which is Better?
Subscribers will also receive two terabytes of cloud storage that typically costs $9.99 monthly, and they will soon gain access to Gemini in Gmail and Google's productivity suite.
The bundle, known as the Google One AI Premium plan, is one of the company's biggest answers yet to OpenAI and its premium chatbot powered by GPT-4. It also shows growing competition among consumers, who now have several paid AI subscription options to choose from.
What happened to Bard AI?
Gemini is built upon Bard's foundation and has replaced the Bard AI mobile app. But while Google is ditching the Bard name, the chatbot itself will not feel much different for most users. It’s got the same design even keeping all previous conversations users had with Bard.
The same goes for all the AI features inside of Google’s Workspace apps like Gmail and Docs, which were previously called “Duet AI” but are now also known as Gemini.
These are the features that help you draft an email, organize a spreadsheet, and accomplish other work-related tasks, and they still serve the same purpose under the Gemini branding.
Bard AI vs Gemini: Which is Better?
Gemini is better than Bard AI in terms of accuracy, nuance, and real-world integration. It’s trained on a much larger and more diverse dataset in comparison, making it better at understanding and generating accurate responses to user queries.
With its Ultra 1.0 model, Gemini Advanced also does a better job than Bard AI with highly complex tasks like coding, logical reasoning, following nuanced instructions and collaborating on creative projects. Gemini Advanced not only allows you to have longer, more detailed conversations; but it also better understands the context from your previous prompts compared to its predecessor.
Gemini also holds the potential to handle more complex tasks that might be challenging for Bard, such as in-depth research or intricate creative writing projects. The model’s architecture is refined to better grasp human language nuances too, resulting in more natural and engaging responses compared to its predecessor.

When AI Content Floods Media
Exposes how low-value AI output exploits attention economics, displaces human voices, and undermines meaningful information ecosystems.
It can access and process information from the real world through Google Search and other services too, providing more relevant and up-to-date responses. This real-world connection enables Gemini to adapt its responses based on the latest information and trends, offering a more dynamic and informative experience.
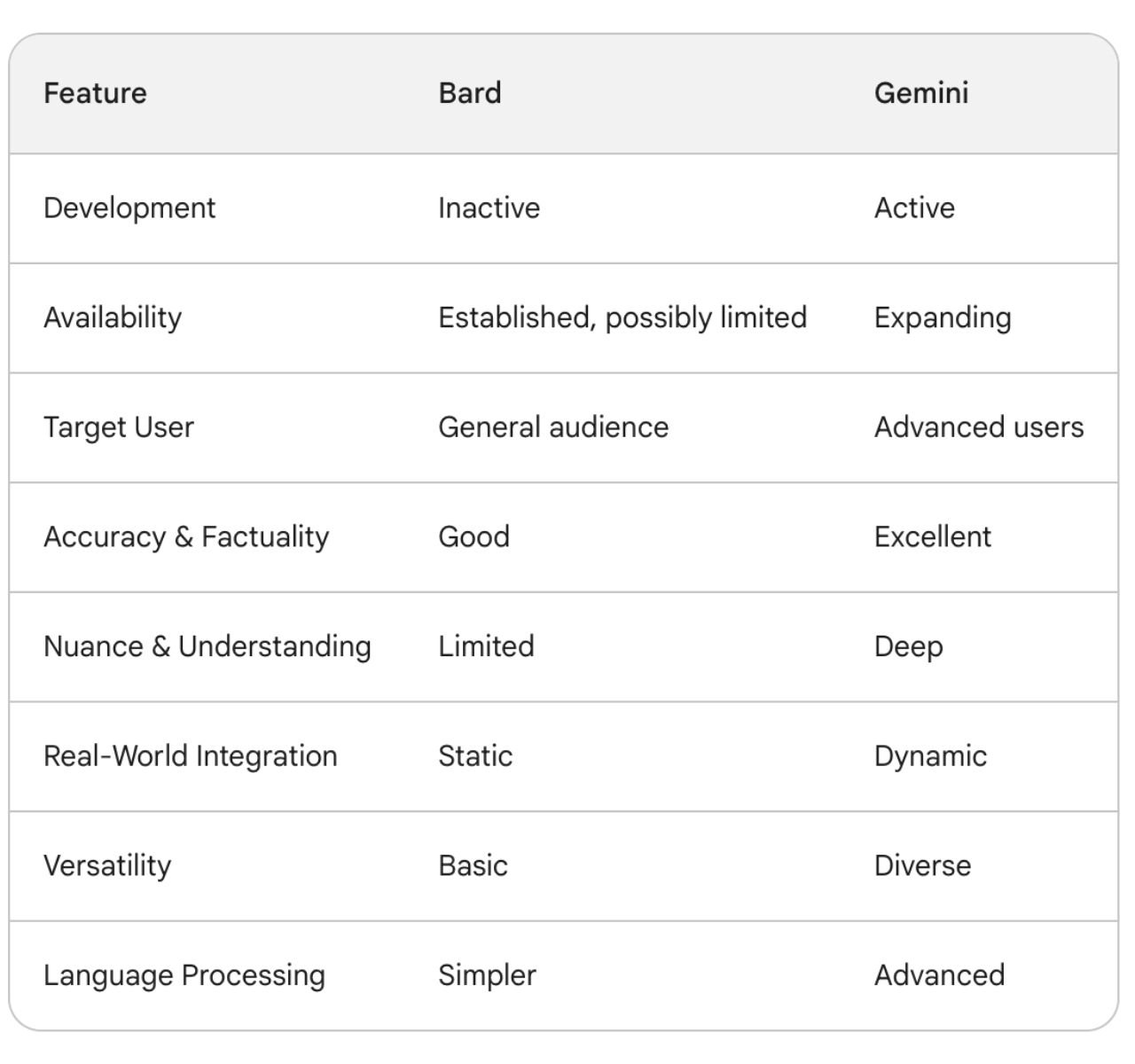
Key differences between Bard AI vs Gemini
Underlying Architecture
Bard AI primarily relied on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), a traditional AI architecture that processes text sequentially, limiting its ability to grasp long-term dependencies and complex relationships between words.
Gemini, however, leverages transformers, a more advanced neural network architecture. Transformers can process entire sentences simultaneously, allowing for a deeper understanding of context, sentence structure, and word relationships. This enables Gemini to better capture humour, sarcasm, and emotional undertones.
Gemini also Possesses multimodal capabilities, meaning it can understand and process various information types like text, images, and audio. This allows Gemini to draw connections between different modalities, leading to richer and more comprehensive responses. Imagine asking about a historical event – Gemini could access and analyze both textual descriptions.
Data and Training
Gemini is trained on a much larger and more diverse dataset than Bard AI. This includes text, code, images, and audio, giving it a broader understanding of the world and language. Bard, however, is primarily focused on text-based data. Gemini also leverages specialized datasets for specific tasks, like high-quality images for visual content generation. Bard relied on more general text sources.
Like Bard AI, Gemini has access to real-time information through Google Search and other services, allowing it to stay up-to-date with current events and trends. Bard's knowledge was static based on its training data.
LLM Pipelines as Dev Platforms
Examines the tooling, guardrails and workflows needed to operationalize vibe coding safely across modern engineering organizations.

Responses
As previously mentioned, Gemini has access to a larger and more diverse dataset than Bard. Pair this with improved processing algorithms, and a refined architecture, and you get responses that are generally more accurate and reliable.
Although Bard could offer informative answers, its factual accuracy wasn't always optimal due to a smaller training dataset and less sophisticated architecture. While capable of generating grammatically correct sentences, Bard sometimes lacked the depth and nuance of human language, sometimes delivering responses that felt more machine-generated.
Natural Language Processing
Gemini leverages more advanced neural network architectures like transformers, allowing for a deeper understanding of language context and relationships between words. Bard, however, used simpler recurrent neural networks, limiting its ability to grasp complex sentence structures and nuances.
Gemini can also process various information types like text, images, and audio, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the world and enabling richer responses. When it comes to text, it emphasizes understanding emotional and cultural contexts, leading to more natural and engaging responses. This ability allows it to capture humour, sarcasm, and emotional undertones in human language. Bard's responses might have lacked these subtleties due to its less sophisticated architecture.

When LLM Power Meets AI Risk
Explore the tradeoffs behind LLM adoption, from bias and misinformation to multimodal capabilities and competitive pressure.
Real-World Integration
Gemini integrates with Google Search and other Google services, enabling it to access and process real-time information from the wider web. This allows it to stay up-to-date with current events, trends, and factual data, providing more relevant and contextually accurate responses compared to Bard.
Bard, on the other hand, on its static training data for information, and its answers were primarily based on its pre-trained knowledge, limiting its ability to adapt to new information or changing contexts.
Availability
Gemini is currently available in over 230 countries and territories, with ongoing efforts to expand further. However, it's not yet universally accessible in all regions and is only limited to English. It seems geared towards users seeking advanced language modelling capabilities. Bard is only available in countries where Gemini has not been rolled out yet.
Final Thoughts
Overall, Gemini surpasses Bard AI in terms of accuracy, nuance, and real-world integration. Its access to a vast dataset and improved architecture leads to better more accurate and reliable responses.
Still, while comparing Gemini and Bard, it's crucial to remember it's not a competition between two separate entities. Bard AI laid the foundation for Gemini's development, serving as a stepping stone in the evolution of language models.
Both models have contributed, and continue to contribute, to advancements in AI and how we interact with technology. Now, being actively developed, Gemini holds immense potential for further advancements in the future of LLMs







Comments ( 1 )
Santino Morela
22/02/2024