With the rise of big data and data-driven decision-making, more and more organisations are turning to geospatial data for more accurate and faster ways to make operational decisions.
The global geospatial analytics market size is expected to surpass the $258.06 billion mark by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 14.1% from 2025.
Geospatial analytics adds timing and location to traditional data types to build data visualisations. These visualisations include maps, graphics, statistics and cartograms showing historical changes and trends from building footprints to transportation networks and more.
At the forefront of the Geospatial data explosion are a number of geospatial data companies mapping a future led by location intelligence.

What is Geospatial Data?
Geospatial data is any data that has a geographic reference. This means it's information that is tied to a specific location on Earth. It's often represented by coordinates like latitude and longitude, but it can also include other spatial information like addresses, ZIP codes, or even shapes like polygons.
Geospatial data is collected through various methods, such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, GPS devices, and ground surveys. It's then processed and analyzed using specialized software to extract valuable insights. This allows maps to add an extra layer of detail to a map meaning that – instead of just seeing the physical features of a place – you can also see information about what's happening there.
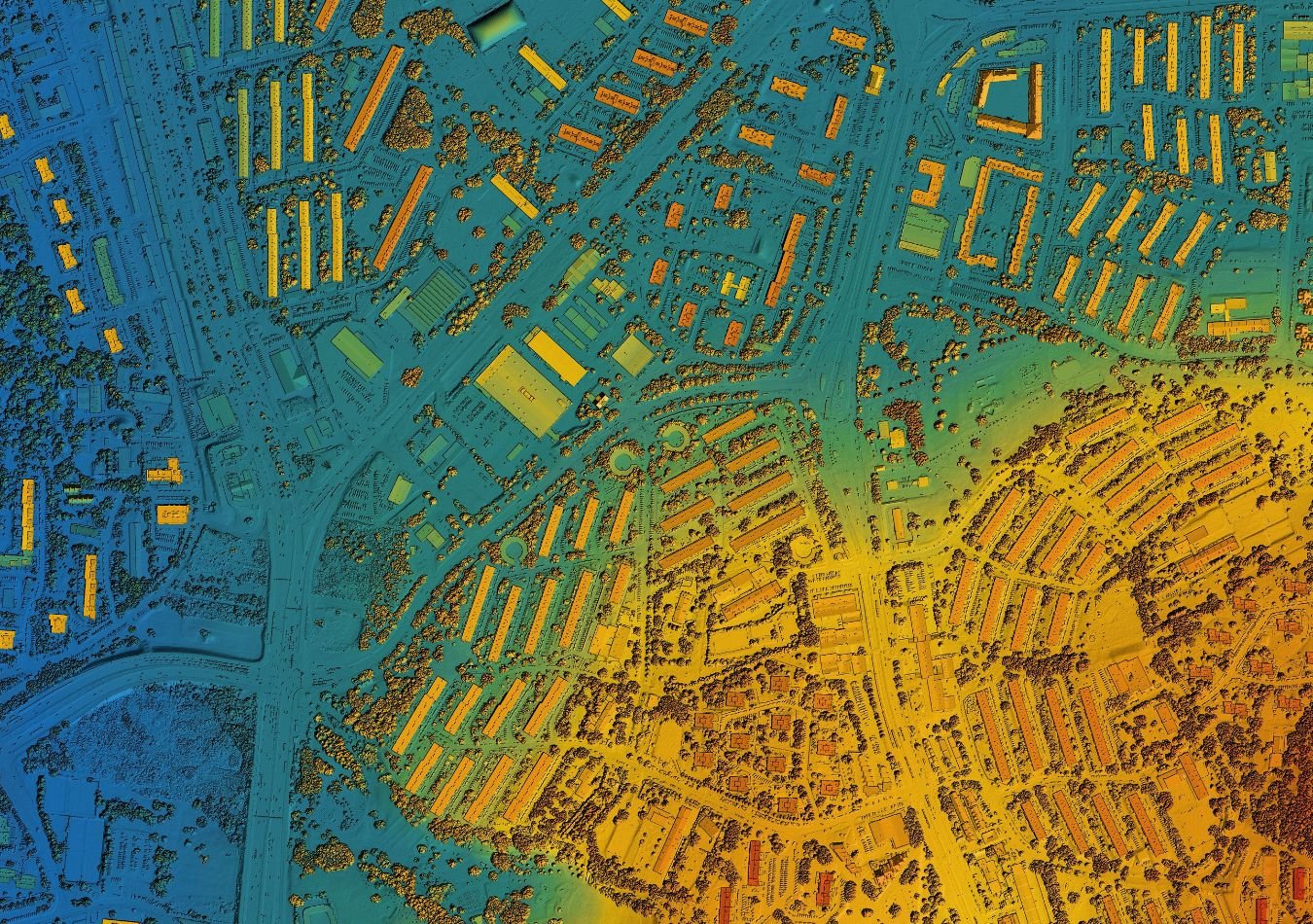
Geospatial data is used in a wide range of applications, from navigation and mapping to urban planning and environmental monitoring. For example, a weather map shows temperature and precipitation data for different locations, while a traffic app provides real-time information on road conditions and traffic flow based on GPS data from vehicles.
What Are Geospatial Data Companies?
Geospatial data companies are businesses that specialise in collecting, processing, analysing, and distributing geospatial data. They offer a variety of services and products related to mapping, location-based services, and spatial analysis.
These companies can provide geospatial data in various formats, such as maps, aerial imagery, satellite imagery, and digital elevation models. They also offer tools and platforms for visualising, analysing, and integrating geospatial data with other types of information.
Geospatial data companies serve a wide range of industries, including:
- Transportation: Mapping and navigation services, traffic management, logistics.
- Government: Urban planning, land management, environmental monitoring.
- Agriculture: Precision agriculture, crop monitoring, land use analysis.
- Telecommunications: Network planning, infrastructure management.
- Insurance: Risk assessment, claims processing.
- Retail: Location-based marketing, store optimisation.
By providing accurate and up-to-date geospatial data and analysis, these companies help businesses make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
Best Geospatial Data Companies

We’re counting down our picks for the top ten best geospatial data companies, ranking each provider based on their impact, innovation and overall reputation in the industry.







Comments ( 0 )