When you think of a black cat, superstition and folklore might come to mind. But in cybersecurity, "BlackCat" represents something far more dangerous.
BlackCat ransomware—also known as ALPHV or Noberus ransomware—is a fast-emerging cyber threat targeting both individuals and organizations. Unlike traditional data breaches that often linger in the shadows of the Dark Web, BlackCat ransomware attacks have become front-and-center in the cybersecurity landscape.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the BlackCat hacker group, including who they are, the industries they target, and the most effective strategies for defending against BlackCat ransomware.

What is BlackCat Ransomware?
BlackCat, also known as ALPHV and Noberus, is a ransomware group that made its debut in mid-November 2021. Known for its sophisticated operations, BlackCat employs the Rust programming language for its payloads, combining the performance of C/C++ with enhanced memory management capabilities. This cyber gang operates by creating public data leak websites on the open internet, compelling victims to pay a hefty ransom to prevent the full exposure of their confidential data.
First detected in 2021, BlackCat stands out for its unprecedented approach: creating public data leak websites accessible on the open internet. This bold tactic aims to coerce victims into paying substantial ransom amounts to prevent the full exposure of their confidential data to the public.
By publicly exposing victims' data and threatening to disclose it unless a ransom is paid, BlackCat strikes fear and uncertainty into the hearts of those targeted. This aggressive approach not only adds urgency to the situation but also amplifies the potential consequences for affected individuals and organisations.
The emergence of the BlackCat gang signifies a noteworthy milestone in the landscape of cyber threats. Particularly striking is their utilisation of the Rust programming language to engineer the payload for their operations. This strategic decision highlights their dedication to optimizing efficiency and resilience in carrying out nefarious activities.
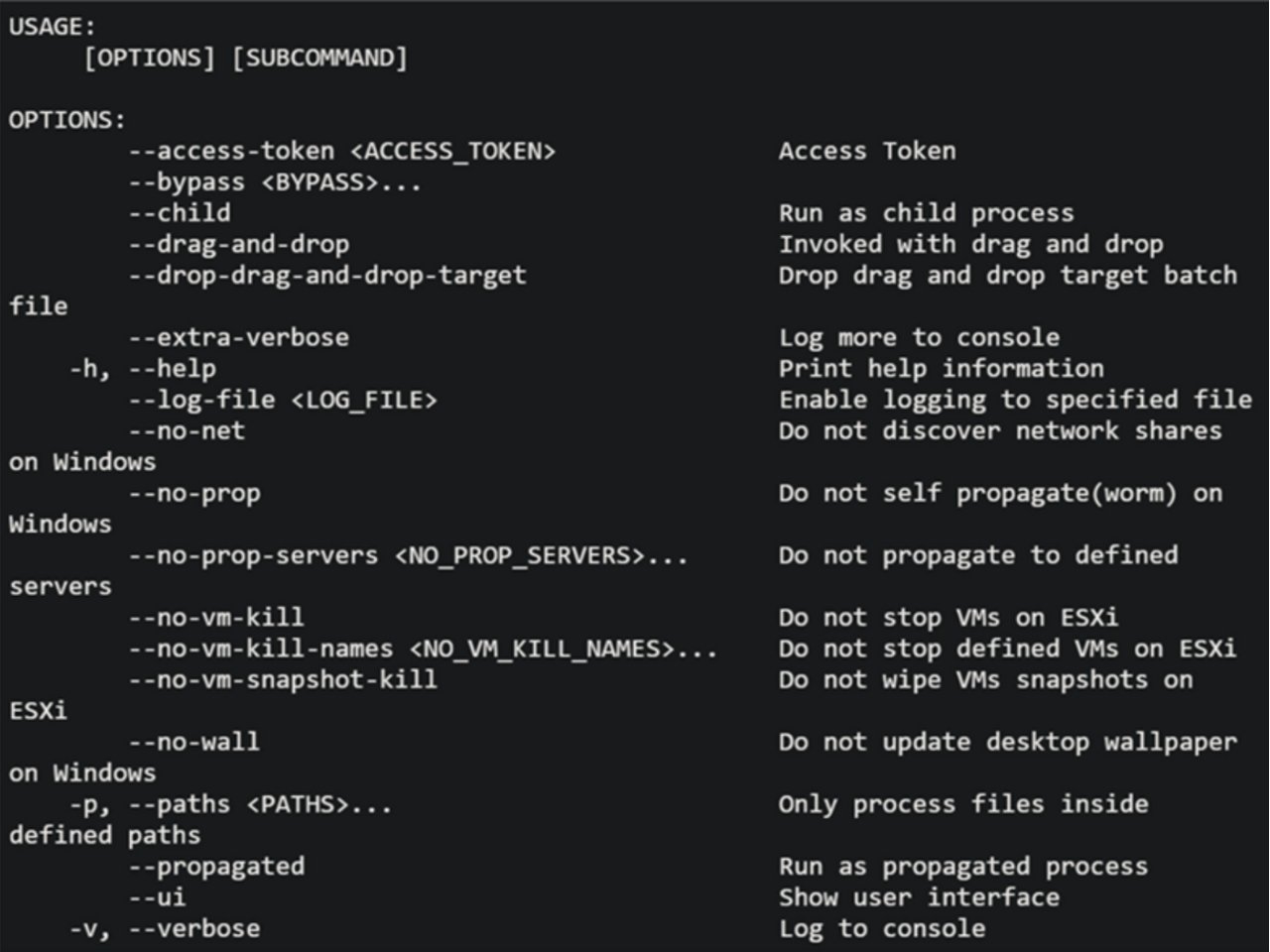
The BlackCat ransomware's sophisticated architecture reflects the cyber gang's meticulous approach to their criminal endeavours. This malware operates with precision, demanding precise access tokens and parameters for execution. Its encrypted configuration file holds detailed instructions, encompassing targeted services and processes for cessation, whitelisted directories, files, and extensions alongside a repository of pilfered credentials from victim environments.
BlackCat is a cybercriminals gang ransomware employs a variety of extortion tactics, with a predominant use of double extortion methods and occasional resort to triple extortion tactics. These tactics involve threatening to disclose stolen data and launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against targeted infrastructure.
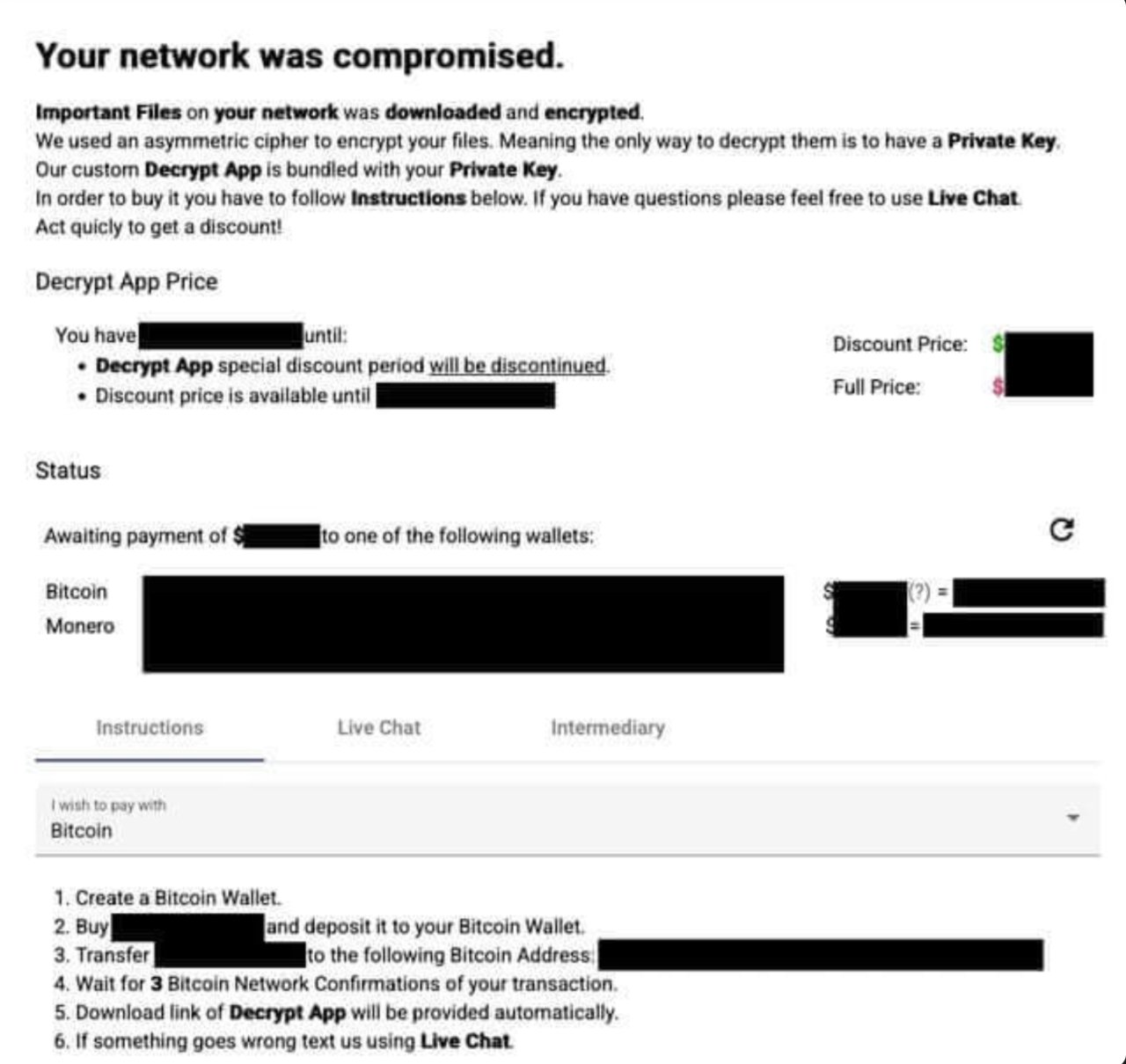
Demands for ransom payments are common in BlackCat ransomware attacks, often amounting to millions in Bitcoin and Monero. Interestingly, some payments are accepted below the initial demand, indicating a degree of negotiation flexibility on the part of the attackers.
Unique Tactics of BlackCat
What sets BlackCat apart from other ransomware groups is its strategic use of public data leak websites. These websites are designed to coerce victims into paying substantial ransom to prevent the complete exposure of their confidential data. By threatening to disclose sensitive information, BlackCat instils fear and urgency, prompting organisations to take immediate action.
The emergence of BlackCat signifies a critical evolution in ransomware tactics. Their audacious approach of publicly exposing victim data not only increases pressure on targets but also elevates the stakes for both individuals and organisations. This double-edged sword of urgency and potential reputational damage enhances the effectiveness of their extortion methods.

When Tech Giants Lose Focus
How leadership churn, portal-era bets and misjudged deals eroded Yahoo’s position in search, media and digital advertising.
The sophisticated architecture of BlackCat ransomware is indicative of the group’s meticulous planning. Operating with precision, the malware requires specific access tokens and parameters for execution. It features an encrypted configuration file that includes comprehensive instructions on targeted services, processes to terminate, and a repository of stolen credentials from victim environments. This intricate design allows for tailored attacks that maximize impact and profitability.
BlackCat employs various extortion strategies, prominently featuring double extortion methods. In some cases, they even resort to triple extortion tactics, which involve threatening to leak stolen data while simultaneously launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against the victim's infrastructure. This multifaceted approach amplifies the pressure on organisations, forcing them into difficult positions regarding ransom payments.
Ransom demands in BlackCat ransomware attacks often reach into the millions, typically requested in Bitcoin and Monero. Interestingly, the group exhibits some negotiation flexibility, occasionally accepting payments below the initial ransom demands. This adaptability reflects their strategic approach to extortion, making them a formidable threat in the world of cybercrime.
What is BlackCat Rust?
Rust is a systems programming language that prioritises performance, reliability, and safety. Developed by Mozilla, Rust is designed to empower developers with the tools needed to build efficient and secure software. Its key features include a strong type system, ownership and borrowing rules that prevent common programming errors like null pointer dereferences and data races, and fearless concurrency, which allows multiple threads to execute without risking data corruption.
The usage of Rust programming language has emerged as a strategic choice for crafting advanced malware like BlackCat ransomware. Renowned for its performance comparable to C/C++ and superior memory management capabilities, Rust provides cyber attackers with a powerful tool to circumvent detection mechanisms and amplify the impact of their operations.
At its core, the operational framework of BlackCat ransomware demands precise execution, requiring an access token consisting of a 32-byte value and other specified parameters. This level of customisation empowers the malware to adapt its behaviour to the intricacies of each targeted system, optimising its infiltration capabilities and amplifying its destructive potential.
Inside a Social Graph Collapse
A case study in weak mobile-era adaptation, algorithm shifts, and feature deprecation eroding network effects in visual platforms.

Furthermore, BlackCat ransomware boasts an encrypted configuration file housing vital operational instructions. These include an exhaustive roster of services and processes slated for termination, directories and files exempted from encryption, and a cache of pilfered credentials harvested from the victim's digital ecosystem. By meticulously fine-tuning these parameters, the BlackCat gang ensures seamless execution of their malicious agenda while mitigating the risk of detection or intervention by security measures.
Key Features of BlackCat Rust
- Strong Type System: Helps catch errors at compile time, enhancing software reliability.
- Ownership and Borrowing Rules: Prevents common programming errors such as null pointer dereferences and data races.
- Fearless Concurrency: Allows safe execution of multiple threads without risking data corruption.
The rise of the Rust programming language has been strategically embraced in crafting advanced malware, such as BlackCat ransomware. Known for its performance that rivals C/C++, Rust offers superior memory management capabilities, providing cybercriminals with an effective tool to evade detection systems and amplify the impact of their attacks.
At the heart of BlackCat ransomware's operations lies a sophisticated framework that demands precise execution. This involves:
- An access token is composed of a 32-byte value and other specific parameters.
- Customisation options enable the malware to adapt its behaviour based on the unique characteristics of each targeted system, enhancing its infiltration capabilities and destructive potential.
Furthermore, BlackCat ransomware is equipped with an encrypted configuration file that contains crucial operational instructions, including:
- A comprehensive list of services and processes scheduled for termination.
- Directories and files are exempt from encryption.
- A repository of stolen credentials obtained from the victim's digital environment.
By meticulously fine-tuning these parameters, the BlackCat gang ensures the seamless execution of their malicious agenda while reducing the likelihood of detection by security measures.
History of BlackCat Ransomware
The cyber gang behind BlackCat's origins date back to the early 2010s when a group of highly skilled hackers began collaborating to develop and distribute various forms of malware. Over time, their operations expanded, and by the mid-2010s, they had established themselves as prominent players in the cybercriminal underworld.

Backdoors, Power and PROMIS
Shows how control of core software can shift from routine procurement to contested power tool, with lethal stakes for those investigating it.
Initially focusing on smaller-scale cyber attacks, such as phishing scams and credit card fraud, the group gradually shifted its focus towards more sophisticated criminal activities, including ransomware attacks. This transition coincided with the rise of ransomware as a profitable business model for cybercriminals, offering the potential for substantial financial gains with a relatively low risk of detection and prosecution.
As the group's operations grew in scope and complexity, they began developing and distributing their custom-built ransomware strains, including BlackCat. Leveraging their expertise in malware development and encryption techniques, they honed their tactics to target high-value entities such as corporations, government agencies, and critical infrastructure providers.
The BlackCat malware first caught the attention of researchers from the MalwareHunterTeam in 2021. By 2022, an FBI advisory linked numerous developers and money launderers to BlackCat, connecting them with two now-defunct ransomware as a service (RaaS) groups – DarkSide and Blackmatter. This revelation highlighted the sophisticated operations of BlackCat and its potential associations with organised cybercrime networks.
The alleged association with DarkSide and Blackmatter, two prominent RaaS groups, provided the cyber gang behind BlackCat with access to advanced tools, resources, and expertise. This collaboration allowed them to expand their reach and amplify their impact, further solidifying their position as a formidable force in the world of cybercrime.
Since its initial detection, BlackCat has undergone rapid evolution, continuously introducing new variants and tactics to circumvent detection and amplify its impact. The malware's creators have demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt, consistently updating their code to exploit vulnerabilities and stay ahead of security protocols.
Despite efforts by law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity experts to disrupt their operations, the cyber gang behind BlackCat has proven resilient, continually evolving its tactics and infrastructure to evade detection and prosecution.
Who does BlackCat target?
In a wave of digital terror that swept through the early months of 2023, BlackCat unleashed a barrage of attacks targeting esteemed organisations worldwide. Among their victims were Grupo Estrategas EMM, NextGen Healthcare, Solar Industries India, Instituto Federal Do Pará, Munster Technological University, and Lehigh Valley Health Network.
When Payroll Becomes an Attack
BA, BBC and Boots breaches show how outsourced payroll and file transfer tools can silently expose banking and identity data at massive scale.

BlackCat's targets encompass a broad spectrum of industries, spanning finance, healthcare, and government sectors. Its typical approach involves infiltrating networks, encrypting data, and demanding substantial ransoms for decryption keys. The financial toll on victims has been staggering, with losses reaching into the millions of dollars.
History of BlackCat attacks
Variant Sphynx (2023)
But the tale took a darker turn with the emergence of a new weapon in BlackCat's arsenal: Variant Sphynx. This sophisticated version, unveiled in February 2023, boasted enhancements designed to enhance its speed and stealth capabilities. Sphynx's deployment marked a significant escalation in BlackCat's capabilities, catching cybersecurity experts off guard and leaving organisations scrambling to fortify their defences.
At its core, Variant Sphynx featured intricate code optimisations that enabled lightning-fast execution and evasion of traditional detection mechanisms. Leveraging advanced obfuscation techniques and polymorphic encryption algorithms, it morphed its signature with each version, confounding even the most vigilant cybersecurity measures.
By May of that same year, the group's reign of terror had left over 350 victims in its wake, a chilling testament to the efficacy of Sphynx's advancements. From multinational corporations to educational institutions and healthcare providers, no sector was spared from the ruthless onslaught of BlackCat's cyber assaults.
As organisations raced to shore up their cybersecurity protocols, the digital battleground was poised for an intensified struggle between defenders and aggressors in the ongoing war against cyber threats. The rise of Variant Sphynx served as a stark reminder of the relentless innovation driving malicious actors in their pursuit of exploiting vulnerabilities in the digital realm.
Reddit Breach (2023)
BlackCat claimed responsibility for breaching Reddit's systems in June 2023, managing to extract a staggering 80 GB of compressed data. Their demands were clear: a ransom of $4.5 million from Reddit. What made this attack stand out was its departure from the group's usual tactics; unlike their typical ransomware campaigns, no data encryption was employed. This left Reddit and its users vulnerable to cyber extortion.
From a technical standpoint, the breach exposed critical vulnerabilities in Reddit's cybersecurity infrastructure, raising questions about the platform's preparedness to fend off sophisticated cyberattacks. Analysts speculated that the attackers exploited weaknesses in Reddit's network architecture or possibly leveraged social engineering tactics to gain unauthorised access. The lack of data encryption further underscored lapses in Reddit's security protocols, underscoring the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Downfall and New Attacks (2023-2024)
On December 19, 2023, the FBI executed a coordinated operation that successfully seized control of the notorious BlackCat ransomware gang's website. Visitors to the group's site were met with a stark message from the FBI: "The Federal Bureau of Investigation seized this site as part of a coordinated law enforcement action against Alphv BlackCat Ransomware. This takedown represented a significant victory in the ongoing battle against cybercrime, with multiple websites confiscated and a decryption tool released by the FBI, enabling ransomware victims to recover their files without succumbing to the demands of cybercriminals.

In the aftermath of this operation, a new chapter in the fight against cyber threats began. The U.S. Department of State announced rewards of up to $10 million for information leading to the identification or location of BlackCat ransomware gang leaders, and an additional $5 million for tips related to individuals involved in BlackCat ransomware attacks. As the world braced for further onslaughts in the ever-evolving landscape of digital warfare, concerns mounted about the resilience of cybercriminal organisations.
Despite the crackdown, the fallout revealed a resilient adversary unwilling to yield to law enforcement pressure. The BlackCat gang quickly regrouped, adopting improvised communication methods to resume their notorious activities. A subsequent FBI advisory highlighted the gang's resurgence, detailing their renewed focus on targeting the healthcare sector in response to intensified law enforcement actions.
The advisory also emphasised the launch of the BlackCat 2.0 Sphynx update, showcasing the group's commitment to innovation and adaptability. This new version featured enhanced defence evasion capabilities and an expanded targeting range that included VMware environments, signalling a concerning escalation in the sophistication of ransomware tactics.
Moreover, ALPHV/BlackCat affiliates continued to utilise advanced social engineering tactics, leveraging legitimate remote access tools and frameworks to infiltrate target networks. Some affiliates even shifted from traditional ransomware deployment to direct data theft and extortion, underscoring the urgent need for organizations to strengthen their cyber defences.
BlackCat Attack Characteristics
BlackCat ransomware attacks are distinguished by their sophisticated tactics and stealthy infiltration techniques. This malware exploits previously compromised user credentials to gain initial access, allowing it to swiftly compromise Active Directory user and administrator accounts.
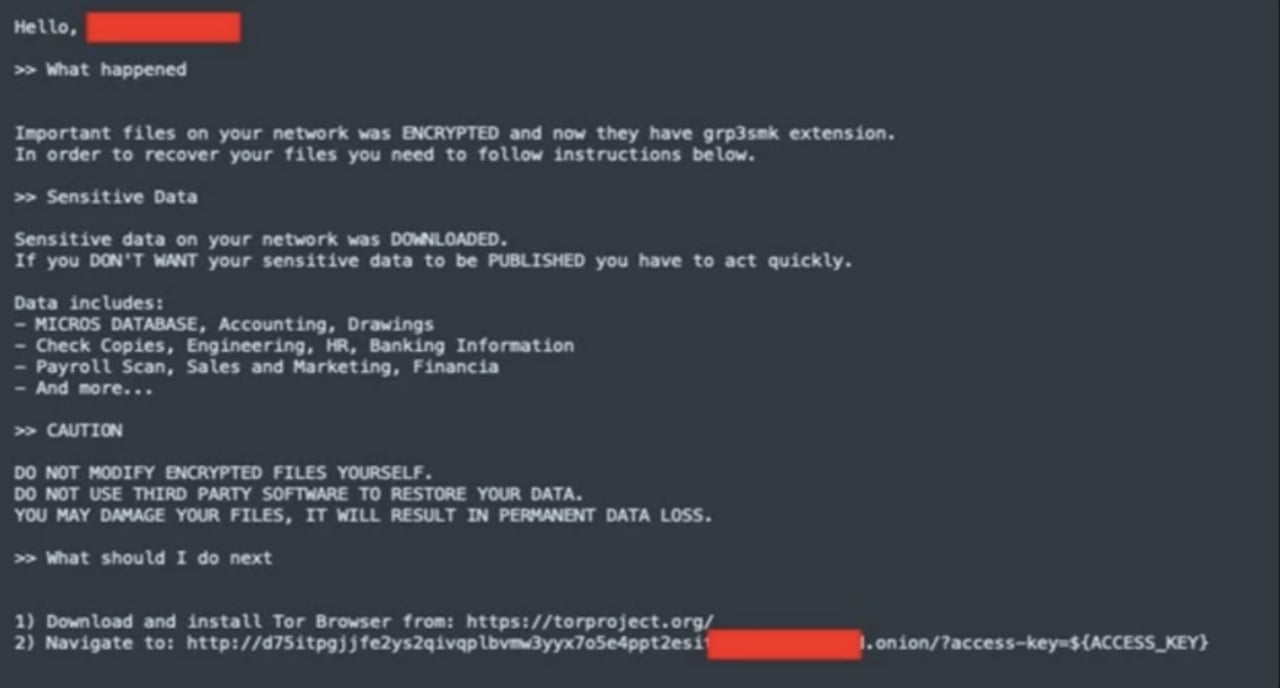
Before deploying the ransomware, BlackCat engages in data exfiltration, stealing sensitive information from victims. This includes valuable data stored in cloud providers utilized by organizations and their clients. The preemptive theft of data adds a layer of coercion, compelling victims to comply with ransom demands under the threat of public exposure or further exploitation of their confidential information.
Similarly, BlackCat members employ sophisticated social engineering tactics and comprehensive open-source research to infiltrate targeted companies. Posing as IT or helpdesk personnel, they utilise phone calls or SMS messages to extract credentials from unsuspecting employees, thereby gaining initial access to the target network. Utilising uniform resource locators (URLs), they engage in live chats with victims to convey demands and kickstart processes for restoring encrypted files.
Once inside a victim's network, BlackCat deploys a suite of remote access software, including AnyDesk, Mega sync, and Splashtop, in preparation for data exfiltration. They establish a user account, "admin," leveraging Kerberos token generation for domain access. Legitimate remote access and tunnelling tools like Plink and Ngrok are employed for lateral movement within the network. To maintain control, they utilise beacons such as Brute Ratel C4 and Cobalt Strike for command and control servers.
By employing the Evilginx2 framework, Blackcat members conduct adversary-in-the-middle attacks, facilitating the acquisition of multifactor authentication (MFA) credentials, login credentials, and session cookies. Passwords obtained from various sources enable further lateral movement across the network. To avoid detection, they leverage allow listed applications like Metasploit while simultaneously clearing logs on the exchange server post-installation on the domain controller.
Data exfiltration and ransomware deployment follow, with the ransom note embedded as a file.txt. Additionally, BlackCat has been reported to employ POORTRY and STONESTOP to terminate security processes. Some affiliates opt to exfiltrate data and extort victims without deploying ransomware, communicating via TOR, Tox, email, or encrypted applications. Subsequently, they delete victim data from the compromised systems.
As part of their extortion strategy, ALPHV Blackcat members offer unsolicited cyber remediation advice post-payment, promising "vulnerability reports" and "security recommendations" to prevent future re-victimization. The resulting encrypted files adopt the naming convention: RECOVER-(seven-digit extension) FILES.txt.
Defending Against BlackCat
When it comes to protecting your organization from **BlackCat ransomware**, implementing effective cybersecurity measures is crucial. Below are key recommendations to enhance your defenses:
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all software is regularly updated with the latest security patches. This proactive step minimizes vulnerabilities that ransomware can exploit.
- Employee Communication and Awareness: Maintain robust communication with employees, stressing the importance of not opening or interacting with suspicious emails. Encourage them to report any phishing attempts or security threats immediately.
- Consistent Data Backups: Implement a reliable backup system to consistently back up server files. Regular backups can mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks and facilitate quicker recovery.
- Utilise Antivirus and Endpoint Detection: Deploy reputable antivirus software and/or endpoint detection and response solutions across all endpoints to identify and neutralise threats.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for all services to add an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Immediate Actions Upon Detection of a Compromise
If a ransomware compromise is detected, follow these immediate steps to minimise damage:
- Isolate Affected Hosts: Disconnect potentially compromised hosts from the network to prevent further spread.
- Reimage Compromised Hosts: Completely reimage affected systems to eliminate any malicious elements.
- Issue New Credentials: Provide new account credentials to all affected users to secure their accounts.
- Conduct a Comprehensive Review: Analyse running processes, abnormal authentications, and recent network connections for any signs of compromise.
It’s crucial to report any compromises or phishing incidents promptly to relevant authorities such as CISA or MS-ISAC. Additionally, file a complaint with the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).







Comments ( 0 )