Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is becoming necessary for securing online accounts, applications and sensitive data. In simple terms, MFA works to offer authorisation to users so they can access these resources and services safely and securely.
Enabling MFA prevents unauthorised access to an account, even in cases of password compromise. This is very important today, as password breaches and attempts at hacking have become common. In other words, MFA supplements two or more verification factors beyond the simple user/password combination to request access to an application or online account.
Given the increase in cyber threats, one must understand why MFA is much needed for protection against the leakage of sensitive personal and enterprise information. However, the big question remains: What is it, though, and how does it work?

This article looks at the importance of MFA in protecting your online accounts and sensitive data. You will learn how MFA works, its crucial role in preventing unauthorised access through multiple verification factors, and generally strengthening your security posture.
How Does MFA Work?
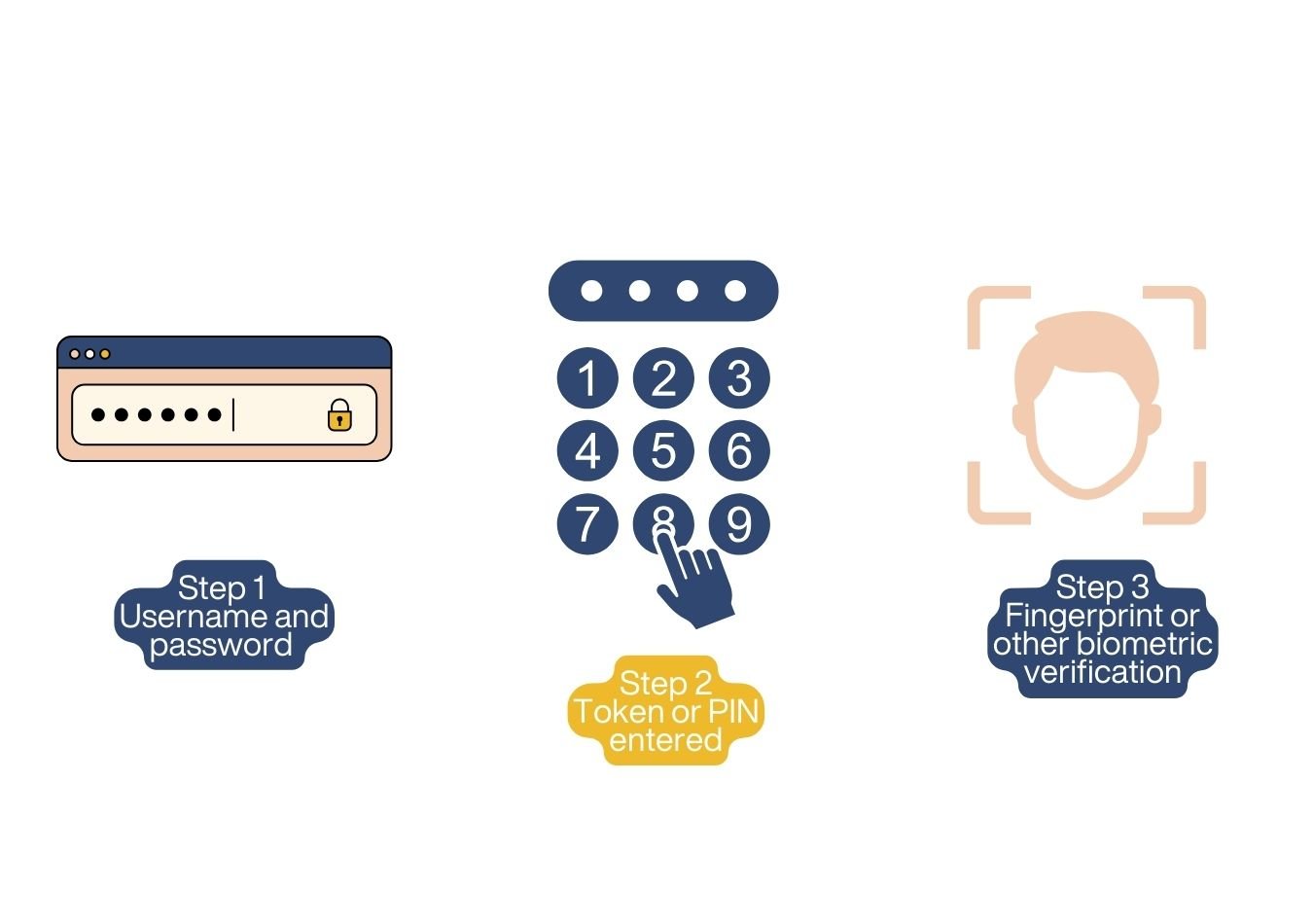
MFA is a multi-step login process. It implies having to sign on more than once; for instance, after typing your password, you will be prompted to use other “factors” such as entering a one-time code emailed or texted to you, answering a security question, or even using biometric authentication fingerprint scanning. By combining different authentication methods, MFA can make it much more difficult for attackers to access your accounts or data.
MFA vs. Two-Factor Authentication: Which Is Different?
There is much speculation on the differences between MFA and two-factor authentication (2FA). Both offer enhanced security, but 2FA is basically a part of MFA. 2FA limits the number of factors involved in the authentication process to two factors only, such as password code, whereas the MFA system can implement two or more factors. Added security flexibility is thus provided by MFA.
Types of MFA Factors
Most of the MFA methods rely on at least one, if not more, of the following information types to authenticate users:
- Something you know - for example, a password or PIN code
- Something you have - a smartphone or a security token
- Something you are - for instance, biometric data such as fingerprints or face recognition.
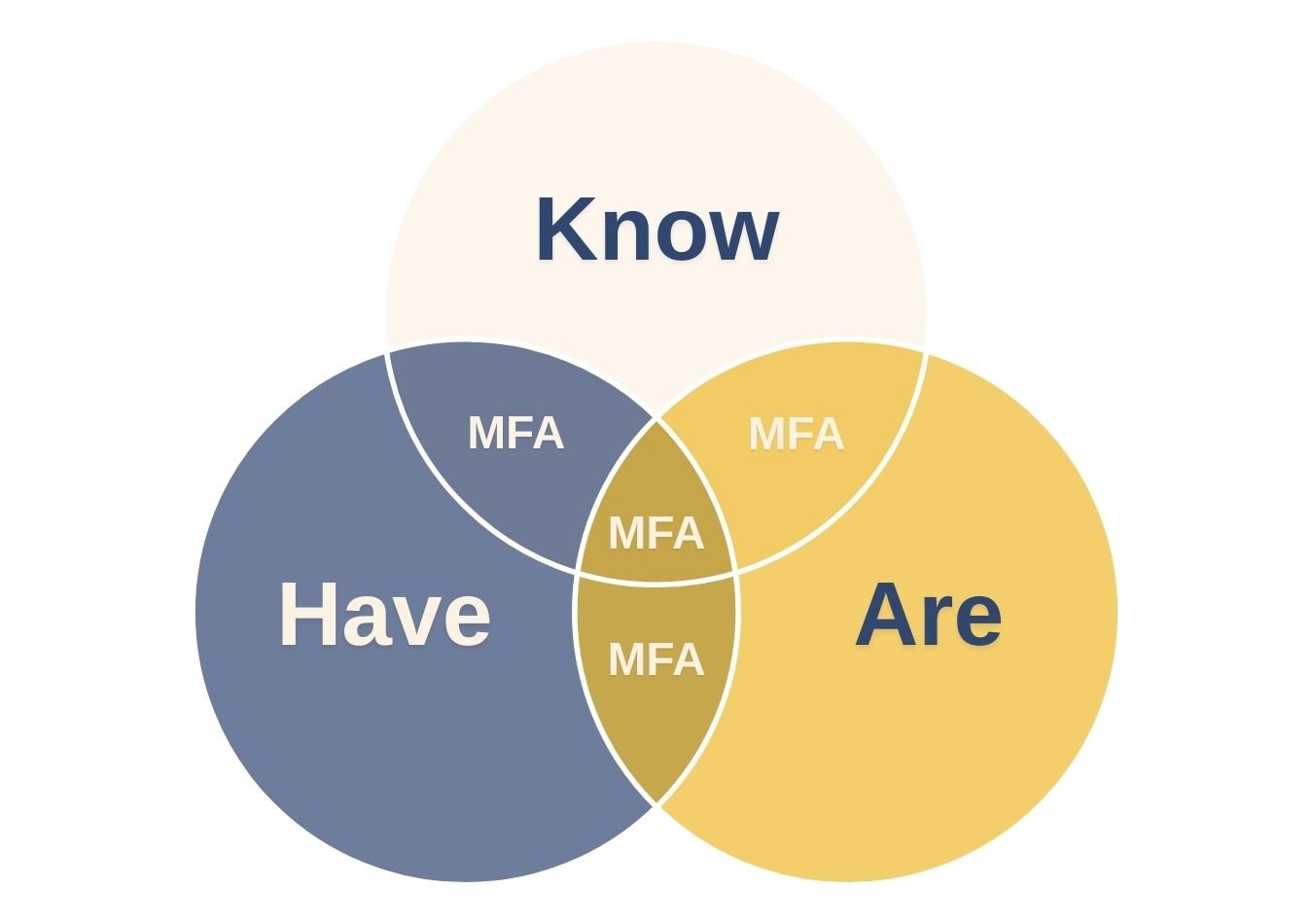
Most MFA solutions combine these elements in various ways to provide even greater security, depending on an organisation's particular security needs. Other advanced forms of MFA include location-based MFA, adaptive authentication, and risk-based authentication.

When AI Agents Reshape Security
Why boards must treat autonomous agents as governance choices and redesign controls around authority, identity, and blast radius.
Adaptive and Risk-Based Authentication
Another cutting-edge feature of MFA is adaptive authentication, which adapts security protocols based on the user’s behaviour or context. Thereafter, it would also ask straightaway for some kind of second factor, such as an authenticator app, to provide additional verification. In this example, however, the user is logging on from an authenticated location at the usual time of day, so it asks only for their password.
Similarly, risk-based authentication takes into account the user's IP address or geolocation to assess the risk related to a login attempt. If there is any mismatch in location, access can be denied, or further verification may be sought. This adaptability is one of the major benefits of MFA, as it prevents unauthorised access without causing much friction to legitimate users.
How to Set Up Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Probably the most common MFA factor is a One-Time Password (OTP). These are usually 4-8 digit codes sent via SMS or email or generated through a Mobile Authentication App. OTPs are time-sensitive; new passwords are generated periodically or whenever one tries to log in.
For example, in order to turn on MFA for Office 365, one will be forced to associate an authenticator application with the account. It means that after your login, the application will generate unique one-time passwords. You take the code and finally log in to your account.
Many users are also searching for how to turn off MFA once it has been enabled. This might be very important once you lose access to your mobile device or authenticator app and won’t be able to log into your account. In most instances, disabling MFA will require one to go back through the account security settings, but this must be done very carefully so that your account stays secure while doing so.
Inside Modern MFA Stacks
Break down the authentication layers, delivery models, and user flows needed to deploy scalable, low-friction identity assurance across the estate.

Benefits of MFA for Enhanced Security
Overall Enhancement of Security Posture
One of the most significant benefits of MFA is that it dramatically enhances an organisation's security by allowing users to validate their identities using more than a simple username and password. That additional layer of protection makes cybercriminals' tasks much more complex, introducing a good measure of defence against cyber threats.
The modern digital space greatly relies on cybersecurity, from the enterprise to the individual levels, as more sensitive information remains online. As a growing number of people rely on cloud services and web-based applications, the potential for data breaches and the misuse of online data has become higher than ever. This can be pretty grave, from money theft to privacy loss.
While passwords are part of a strategy to secure online accounts, they cannot serve alone anymore. Weak or reused passwords are easily manipulated by cybercriminals, who thus gain unauthorised access to several accounts. MFA involves another layer of security that can prevent such cases from happening in the first place.

Ranking 2025 Zero Trust Leaders
Compare 10 enterprise-ready vendors on identity integration, policy automation, performance and governance to align security with strategy.
Reduced Security Risks
Probably the most significant advantage of MFA is that it reduces security risks. Since MFA applies to various layers of verification, the probability of human error, misplaced passwords, or even stolen devices that will lead one’s account to be compromised is minimised. Entreprises will be able to adopt digital transformation initiatives with assurance and confidence in the knowledge that MFA keeps organisations and customer data safe through online interactions and transactions.
Security Response Improvement
Implementing MFA enhances the ability to detect and respond to cyber threats. Suppose the MFA systems are configured to show alerts upon detecting suspicious login attempts. This helps organisations respond on time to minimise potential damage. Real-time response is one of the big advantages of MFA, as it enables the business to keep ahead of cyber threats.







Comments ( 0 )