Staying secure and private online has never been trickier in 2024. With an estimated 353 million Americans impacted by data compromises in 2023 alone, your personal and sensitive data is constantly stolen without you even noticing.
And in an age where websites are collecting your data from every click – whether it be the IP addresses, browser history or demographic information – your data is never really private no matter how safe you stay on the internet.
Many organizations and individuals have turned to proxy servers and VPNs to keep their data secure and out of the hands of the websites they visit. But while these two privacy solutions suit the same purpose, their method of keeping your private data locked away is entirely different.
This article delves into some of the key differences between a proxy server vs VPN to help you choose which one is best for you or your organization in 2024.

What is a proxy server?
A proxy server is an intermediary server that sits between your device and the internet. When you visit a website, your request doesn't go directly to the website's server, but to the proxy server first. The proxy server then fetches the information you requested from the website and sends it back to you.
Without a proxy, your device requests traffic from the web directly as it would on a standard connection. Instead of your computer directly contacting websites, it goes through the proxy server first, which fulfils your requests and acts as a gatekeeper of sorts.
It's important to remember that proxy servers typically don't encrypt your data by themselves. While they offer privacy benefits by masking your IP for strong encryption, they don’t encrypt your data like some other online privacy tools and solutions.
There are a few reasons why you might use a proxy server. One reason is to improve privacy. Because the website only sees the proxy server's IP address, not your own, it can be harder for the website to track your activity.
Another reason is to bypass geo-blocking. Proxy servers located in different countries can be helpful for accessing websites are only available in certain countries. For example, if a streaming service restricts certain shows to specific regions, a proxy server in a permitted region could potentially allow you to access that content.
Some of the top proxy servers available today can also filter out malicious content or websites, offering an extra layer of protection against malware and phishing attempts. Organizations can use them to restrict employee access to certain websites or manage internet usage within their network too.
Features of proxy servers
1. IP Masking
Normally, when you visit a website, your computer communicates directly with the website's server, revealing your device's IP address. This IP address acts like a unique identifier, potentially revealing your location and internet service provider.
With a proxy server, your computer first sends its request to the proxy server. The proxy server then acts on your behalf, fetching the information you requested from the website's server.
The website server only sees the IP address of the proxy server, not your own. This effectively masks your identity and makes it more difficult for the website to track your activity or pinpoint your location.
2. Security
By hiding your real IP address, proxy servers make it more difficult for hackers to target your device directly. Without your IP address, malicious actors can't exploit vulnerabilities specific to your system or bombard you with targeted attacks.
Certain types of proxy servers, like HTTPS proxies, can also encrypt the communication between your device and the proxy server itself. This adds an extra layer of security for the data being transmitted, making it more difficult for eavesdroppers to intercept sensitive information.
3. Geo-location Bypassing
Many websites and services use your IP address to determine your location. If your IP indicates you're in a region where the content is blocked, you're met with a frustrating "access denied" message.
When you use a proxy server, your internet traffic gets routed through that server first.The proxy server has its own IP address, likely based in a different location than yours. So, when you try to access a geo-restricted website, the website sees the proxy server's IP, not your own.
4. Content Filtering
Some proxy servers can be configured to act as a basic security wall. They can be programmed to identify and block access to websites known to be malicious or harbour malware, phishing, and other security threats. This adds an extra layer of protection before potentially harmful content reaches your device.
5. Bandwidth Management
Proxy servers can be helpful tools for managing bandwidth consumption on a network, particularly for organizations or institutions with multiple users.
When users within the network request the same webpage or file repeatedly, the proxy server can store a copy of that data. Subsequent requests for the same content can be fulfilled from the cached data on the proxy server, reducing the need to download it again from the original source. This saves bandwidth and improves loading times for users.
Network administrators can also leverage proxy servers to manage bandwidth allocation for different users or applications. They can prioritize essential traffic like work-related websites or video conferencing tools while limiting bandwidth for less critical activities like social media or online gaming. This ensures optimal use of available bandwidth for the most important tasks.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or virtual private network, is a service that helps you securely connect to the internet. It works by creating a private tunnel between your device and a remote server operated by the VPN provider, encrypting your data in the process.
With a VPN, all your internet traffic travels through this encrypted tunnel, making it difficult for anyone to snoop on your activity or steal your data.
By encrypting your data, a VPN also helps to protect you from man-in-the-middle attacks, where someone tries to intercept your communications. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi, as these networks are often not secure and can leave you at the mercy of malicious actors.

Like proxy servers, VPNs also mask your IP address, which is a unique identifier that can be used to track your location and online activity. Your internet traffic appears to be coming from the VPN server's location, rather than your own.
It's important to remember that VPNs are not a foolproof security solution. They can also slow down your internet connection and some websites may block traffic from known VPN servers.
Key features of VPNs
1. Data encryption
When you connect to a VPN, your device connects to the VPN server. This involves exchanging keys that will be used for encryption and decryption. Once the keys are exchanged, your device uses an encryption algorithm to scramble the data you want to send.
Common algorithms used by VPNs include AES-256, which is considered highly secure. The encryption process transforms your readable data into a seemingly random string of characters, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it.
2. Data leak protection
Even with a VPN, data leaks can occur, exposing your real IP address or DNS requests. A VPN constantly checks for discrepancies between your internal IP address and your external IP address. If a mismatch is detected, the VPN might automatically disconnect your internet connection to prevent further data exposure.
The VPN routes your DNS requests through its own private DNS servers instead of your ISP's servers. This ensures your browsing activity remains hidden from your ISP.
3. Kill Switch
VPN connections, while reliable, aren't perfect. Temporary glitches, software updates, or even a momentary internet hiccup can cause the VPN tunnel to collapse. The kill switch, prevents your device prevents your device automatically reverting to using your regular internet connection and potentially exposing your real IP address, browsing activity, and other sensitive data for that brief period.
4. Split Tunneling
VPN split tunnelling is a feature that allows you to have more control over how your internet traffic is routed. With a traditional VPN, all your internet traffic is encrypted and sent through the VPN server. This can be great for security and privacy, but it can also slow down your internet connection and make it difficult to access local network resources.
Split tunnelling lets you choose which traffic goes through the VPN tunnel and which traffic bypasses it and travels directly over your regular internet connection. This gives you more flexibility and can be useful in a variety of situations.
5. No-log policy
A VPN's no-log policy is a promise by the VPN provider that they don't collect or store any data about your online activity while you're connected to their service. In some countries, governments have the authority to compel VPN providers to hand over user data. With a no-log policy, even if the VPN provider is legally obligated to cooperate, they wouldn't have any data to provide.
Many companies also track your online activity to build a profile of your interests and bombard you with targeted advertising. A no-log VPN prevents your VPN provider from collecting this data, making it harder for advertisers to track you across the web.
Proxy vs VPN: What’s the Difference?
Proxy servers and VPNs are both tools that can be used to mask your IP address and browse the web more anonymously.
But while VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic, creating a secure tunnel between your device and the VPN server, proxy servers simply hide your IP address. This means proxies can’t encrypt your personal data in the same way VPNs do.
Proxy servers function at the application level. You can configure them to work with specific browsers or applications, but they won't encrypt or anonymize all your internet traffic. VPNs, however, work on the operating system level and encrypt all your traffic, regardless of the application or website you're using.
Of course there are a number of other differences to consider when choosing a proxy server or VPN for your business. Here’s a more detailed look at of some of the key differences between proxies and VPNs below:
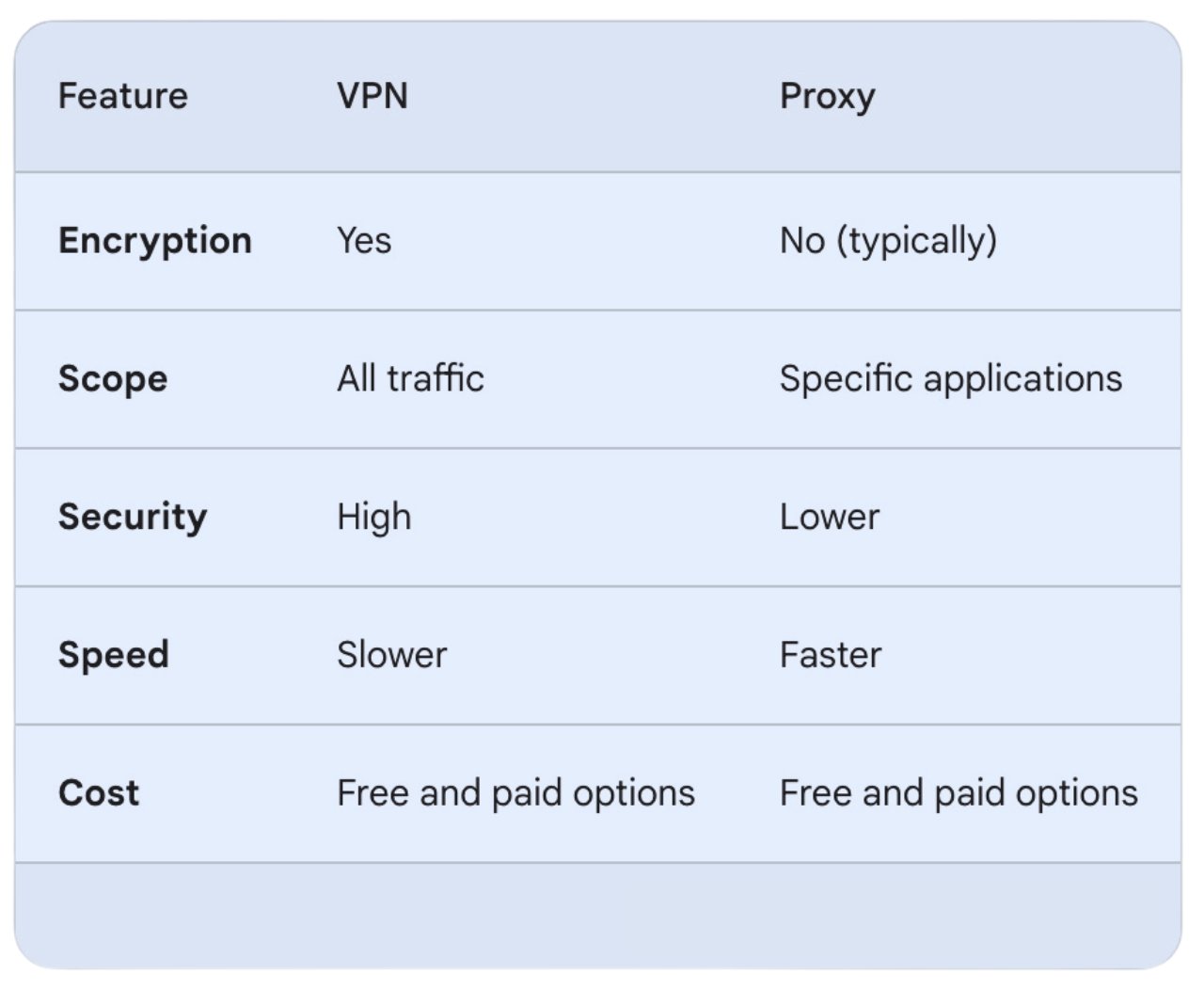
Key Differences
1. Encryption
With a VPN, your data is scrambled, making it difficult for unauthorized users to decipher it. This encryption is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks or accessing sensitive information online (like banking details or medical records).
But proxy servers don’t typically encrypt your data like VPNs do. Think of a proxy server as a middleman that forwards your requests to websites. It hides your IP address from the website you're visiting, but your data travels in the open. This means anyone monitoring the network traffic can potentially see what information you're sending and receiving.
There are some proxy services that offer encryption, but they are less common than standard proxies. Even with encryption, a proxy server might not offer the same level of security as a VPN because encryption protocols and overall security practices can vary.
2. Scope
A VPN acts like a secure tunnel. All your internet traffic gets routed through this tunnel, regardless of the application or website you're using. This means your entire online activity is encrypted and your IP address is masked for everything you do online.
Proxy servers, however, work on a more selective basis, and can be configuredto work with specific programs, like your web browser. Traffic from that program will be routed through the proxy server, hiding your IP address for those specific actions. However, any other applications on your device will continue using your normal internet connection and IP address.
3. Security
As previously mentioned, VPNs Use encryption to scramble your internet traffic. This makes your data unreadable to anyone who intercepts it, like hackers on public Wi-Fi, your internet service provider (ISP), or even government surveillance.
Proxy servers, however, typically don't encrypt your traffic. While they reroute your traffic and hide your IP address, the information itself travels unencrypted. This means that VPNs are generally more secure than proxy servers.
VPNs may also offer extra security features like kill switches and DNS leak protection that proxies servers don’t have. DNS leak protection ensures your DNS requests (used to translate website names to IP addresses) are also routed through the VPN, further protecting your privacy. Meanwhile, a kill switch automatically cuts off your internet connection if the VPN connection drops, preventing your data from being accidentally exposed.
4. Speed
VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic before sending it through the VPN server. This encryption process adds an extra layer of security, but it also requires additional processing power and can slow down your connection. Proxies, on the other hand, typically don't encrypt your traffic, so there's no encryption overhead to slow things down.
This means that proxy servers are often faster than VPNs, especially if the proxy server is located closer to you compared to the VPN server you're connected to. The distance to the VPN server can significantly affect speed. Connecting to a VPN server further away adds latency (delay) to your connection.
5. Cost
Cost can vary when it comes to proxies and VPNs. But proxy servers are generally considered cheaper than VPNs, with many of them being free to use. Free VPNs exist too, but they come with significantly more limitations than free proxy servers do. They often have data caps, restrict server locations, and might throttle your connection speed.
Some free VPNs have been known to inject malware or track your activity. It's generally not recommended to rely on free VPNs for security or privacy.
Paid VPNs are the most reliable and secure option. Prices can vary depending on the provider, features offered, and subscription length. Generally, you can expect to pay between $3 and $12 per month, with some premium services costing even more.
Proxy server vs VPN: Which is better?
There's no single better option between proxy servers and VPNs, as it depends on your specific needs. VPNs hide your IP address and encrypt your traffic, making your online activity invisible to hackers. Proxy servers only hide your IP address, but they offer faster speeds and cheaper costs at the price of less security.
Choose a VPN if:
- Security and Privacy is crucial. VPNs encrypt your traffic, making your online activity invisible to snoopers and hackers. This is crucial for tasks like online banking, using public Wi-Fi, or accessing sensitive information.
- You Need to Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs offer a wide range of server locations, allowing you to virtually change your location and access content restricted in your region.
- You Want Consistent Performance. Paid VPNs typically invest in good infrastructure to provide reliable and fast connections.
Choose a Proxy if:
- Speed is Your Top Priority. Proxies generally offer faster connection speeds compared to VPNs due to the absence of encryption overhead. This can be beneficial for tasks like streaming video content.
- You Only Need to Bypass Basic Geo-restrictions. Free or low-cost proxies might be sufficient for simple tasks like accessing websites blocked in your region. However, be cautious of their limitations.
- Cost is a Major Concern. There are many free proxy options available, while most reliable VPNs require a subscription.







Comments ( 0 )