Data has become an essential asset for businesses. Not only does it drive innovation, improve decision-making, and shape organizational processes, but it also ensures competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving business world.
But effectively managing this valuable resource is easier said than done. According to a study by Seagate, Just 32% of data available to enterprises is put to work, leaving 68% of organizational data unleveraged in a world where data is central to business success.
When organizations fail to leverage their most valuable data, they miss out on an opportunity to outperform competitors in areas like product development, customer satisfaction, and marketing ROI.
Managing this data effectively throughout its entire lifecycle—from creation to disposal—is crucial to ensuring its accuracy, security, and compliance with regulatory standards.
This is where Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) comes into play.
This article tells you everything you need to know about DLM, including what it is, how it works, and how it can help you better manage your data assets.

What is data lifecycle management (DLM)?
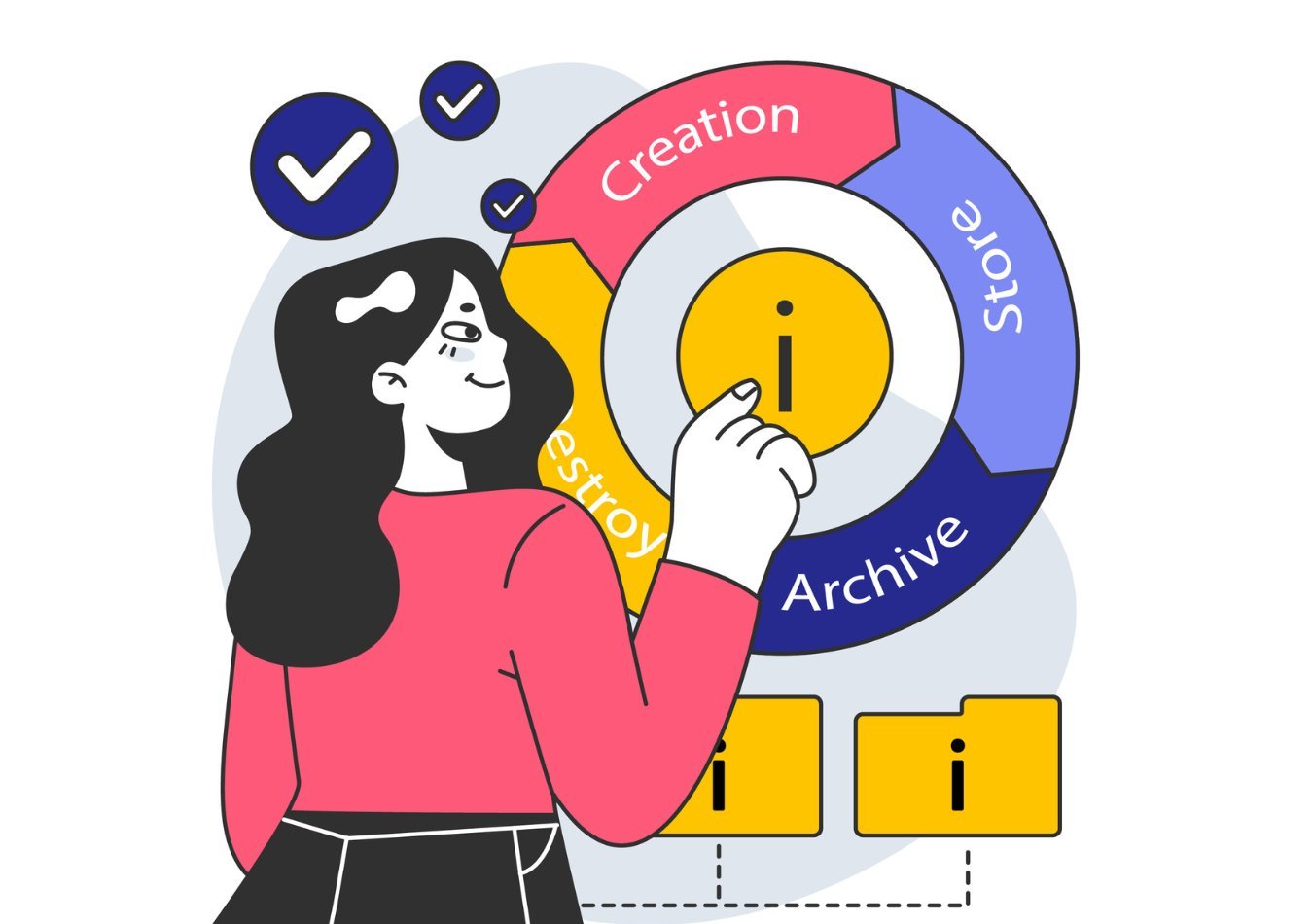
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a strategic approach to managing data throughout its entire existence, from creation to disposal. It involves a systematic process of planning, organizing, storing, protecting, and ultimately disposing of data in a way that aligns with an organization's business objectives and regulatory requirements.
The goal of DLM is to optimize the management of data, ensuring that organizations can store, access, and analyze data effectively while reducing costs, minimizing risks, and protecting sensitive information. The data lifecycle typically includes several key stages: creation, storage, usage, sharing, archiving, and deletion. During each stage, different considerations come into play.

For example, in the creation stage, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data is critical. In the storage phase, organizations must decide where and how to store data, balancing cost, security, and accessibility.
DLM can also help organizations unlock the full potential of their data by making it more accessible for analysis, thereby driving better decision-making and enabling data-driven innovation. It also helps businesses streamline their operations, mitigate the risk of data breaches, and ensure that they remain compliant with industry standards and data protection laws, such as the GDPR or CCPA.
5 Stages of data lifecycle management (DLM)
1. Data Creation
The lifecycle begins when data is generated or acquired. This can happen in various ways, such as user input, system-generated logs, transactional records, or external data imports. At this stage, ensuring data quality is paramount—data should be accurate, complete, and reliable. Proper classification of data based on sensitivity or usage is often applied, as this influences how the data will be handled in subsequent stages. Additionally, metadata (data about the data) is often added to facilitate future tracking, searching, and management.
-
Data Storage
Once created, data needs to be stored securely and efficiently. In this stage, organizations must determine how and where to store the data, balancing factors like accessibility, cost, and compliance. Depending on the type of data, it may be stored in databases, data warehouses, cloud platforms, or on-premise servers. Data encryption and backup strategies are key considerations in this phase to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, or loss. Efficient storage also helps to minimize unnecessary costs by utilizing tiered storage options, where less critical data may be stored on cheaper, slower media.
3. Data Usage
After storage, data moves to the usage stage, where it is accessed, processed, and analyzed to support business operations or decision-making. Proper access control is vital to ensure that only authorized personnel can view or manipulate the data. During this stage, maintaining data integrity is crucial, as data can be modified or transferred between systems, departments, or external parties. Ensuring that data is accurate and up-to-date at all times is essential for its effective use, whether for generating reports, driving machine learning models, or providing insights for decision-makers.
4. Data Archiving
As data ages, it may become less frequently accessed but still needs to be retained for legal or business reasons. In the archiving stage, data is moved to long-term, secure storage. Archived data is typically stored in a less expensive format but must remain accessible if needed for audits, legal proceedings, or historical analysis. A key challenge here is maintaining the ability to retrieve archived data quickly and reliably while ensuring that it remains protected from unauthorized access or accidental deletion.
5. Data Disposal
The final stage of the data lifecycle is disposal, where data is no longer needed and is securely deleted or destroyed. It is important that this process is conducted according to legal and regulatory requirements, particularly for sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII). Proper data disposal reduces storage costs and limits the risk of data breaches from outdated or unused information. Techniques like data wiping, shredding, or degaussing (in the case of physical media) are used to ensure that deleted data cannot be recovered.
Why is data lifecycle management important?
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is crucial for ensuring the security and integrity of data throughout its lifespan. throughout its lifespan. As data passes through various stages—creation, storage, usage, sharing, and eventual disposal—it faces significant risks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Implementing strong DLM processes ensures that data is protected with appropriate safeguards like encryption, access controls, and auditing at every stage, reducing vulnerabilities and helping organizations respond effectively to security threats.
DLM also plays a crucial role in helping businesses comply with legal and regulatory frameworks such as the GDPR and CCPA, helpsing organizations implement processes that align with these legal requirements and ensuring they remain compliant.
For this to happen, data must remain accurate, complete, and accessible as it is created and used within an organization. DLM ensures that data quality is maintained across its lifecycle, enabling businesses to make decisions based on reliable, timely information and improve operational efficiency.
What are the benefits of data lifecycle management?
1. Data Security and Risk Mitigation
One of the primary reasons DLM is important is that it helps organizations safeguard sensitive data. As data passes through various stages—creation, storage, usage, and sharing—it becomes vulnerable to risks such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. DLM ensures that security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, are applied at each stage, minimizing the risk of data exposure. A well-implemented DLM strategy reduces vulnerabilities and enhances an organization’s ability to detect and respond to security threats promptly.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Organizations today face a complex landscape of data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to hefty fines, legal consequences, and reputational damage. DLM ensures that data is handled in accordance with relevant laws throughout its lifecycle. For instance, sensitive data like personally identifiable information (PII) can be properly classified, monitored, and disposed of, while audit trails can be maintained to demonstrate compliance during regulatory reviews.
3. Optimizing Data Storage and Reducing Costs
As businesses generate more data than ever before, the costs associated with storing, managing, and retrieving this information can quickly escalate. DLM helps organizations optimize their data storage strategies by ensuring that data is stored in appropriate locations based on its relevance, frequency of use, and sensitivity. For example, active data may be stored in high-speed, expensive environments, while archived or less frequently accessed data can be stored on lower-cost, long-term storage solutions. By employing tiered storage and regularly reviewing data retention policies, DLM reduces unnecessary storage expenses while ensuring that valuable data remains accessible.
4. Improving Data Quality and Usability
The value of data is directly linked to its accuracy, relevance, and usability. Poor data quality can lead to flawed insights, incorrect decision-making, and wasted resources. DLM ensures that data quality is maintained throughout its lifecycle by applying processes such as validation, cleansing, and regular monitoring. It also ensures that only authorized personnel have access to modify or delete data, reducing the risk of accidental errors or unauthorized changes. By enforcing strong data governance practices, DLM improves the reliability of the data that organizations rely on for analysis and strategic decision-making.
5. Efficient Data Retention and Disposal
Retaining unnecessary data not only increases storage costs but also exposes organizations to greater risk in the event of a data breach. DLM ensures that data retention policies are clearly defined, allowing organizations to archive data for future reference or delete it in a secure and compliant manner when it has outlived its usefulness. Proper data disposal also helps businesses avoid the consequences of holding nto outdated or irrelevant data, which can clutter systems and impede efficiency.
6. Enhancing Business Agility and Decision-Making
In today’s data-driven world, organizations must be able to quickly access and leverage data to remain competitive. DLM ensures that data is organized, secure, and accessible when needed, enabling businesses to make informed decisions faster. By maintaining high-quality data and ensuring that it flows smoothly through its lifecycle, DLM enhances the ability of businesses to respond to market changes, customer demands, and emerging opportunities. This increased agility is crucial for fostering innovation and driving growth in the digital economy.
DLM vs ILM (Information Lifecycle Management): What’s the difference?
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) and Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) both focus on managing data, but they differ in scope and approach. DLM specifically addresses the management of data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal, with a focus on optimizing storage, ensuring security, and maintaining compliance. ILM, on the other hand, has a broader scope, encompassing not just data but all forms of information, including documents, emails, and media.
While DLM is more technical, focusing on data handling and storage, ILM incorporates how information is used within the organization to support business processes and decision-making.
ILM looks more at the relevancy and accuracy of the information being managed. While DLM operates on the entire file, ILM looks at the type of information within the file. While DLM products manage files based on their type, shape, maturity, and size, ILM solutions allow businesses to search for specific files and understand the information within them.






Comments ( 0 )