Article contributed by ManageEngine

Why aren't passwords enough to protect your data against theft?
Passwords are pivotal in guarding resources but as a standalone authentication factor, they cannot guarantee security.
Employees tend to set weak, easy-to-remember passwords which might put the organisation's security at risk. They are also prone to making other common password mistakes such as repeating passwords for multiple resources, storing passwords in plain sight, and retaining the same password for an extended duration. All these reasons make passwords vulnerable to numerous password attacks such as phishing, brute-force, keylogging, and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
Cybercrime techniques and rates have evolved tremendously in recent times, cautioning IT admins to guard privileged or administrator user accounts more carefully. If an attacker happens to steal the credentials of any of these accounts, they’ll have access to the most important data and resources in the network, and the consequences can be devastating.
To reduce all such risks, organizations must protect their resources with multi-factor authentication on top of passwords.
What is MFA and how does it work?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is the process of verifying a user's identity with multiple authentication factors before they are given access to a resource. These authentication factors may include something they know (knowledge factor), something they have (possession factor), and something they are (inheritance factor).
- Knowledge factor:
The knowledge factor includes information that only a legitimate user should know. This information may be passwords, PINs, passphrases, or answers to security questions.
- Possession factor:
The possession factor includes authentication that is performed with something the user possesses, like a mobile phone, a physical token, or a smart card.
- Inheritance factor:
The inheritance factor involves verifying the user's identity using inherited biometric characteristics, like fingerprints or through , retinal, or vocal recognition.
The location and time factors are also gaining much importance today. The location factor verifies that subsequent access attempts by a user are not from two completely different locations. The time factor checks the user's access request time and prompts additional authenticators if the access request time is different from the usual.
What are adaptive MFA and conditional access techniques?
In adaptive MFA (also known as risk-based or context-based MFA), users are provided with authentication factors that adapt each time they log in. Which factors are used depend on an AI-determined risk score of the user, which is calculated based on contextual information such as the number of consecutive logon failures, the user account and user role category, and the physical location (geolocation) of the user requesting access. This contextual information can be pre-configured as conditions based on which access decisions are made, thus giving this technique the name conditional access.
Adaptive MFA improves the security posture of an organisation and helps create a Zero Trust environment.
Benefits of implementing MFA
The following are some benefits that you can enjoy when you implement MFA in your organisation:
- Secures identities and resources of an organisation, and is easy to implement.
- Protects against breached passwords and stolen user devices
- Helps build a secure environment and comply with data compliance regulations like the GDPR, the PCI DSS, HIPAA, and NIST 800-63B
What to consider while implementing MFA
The following are some things to consider before you implement MFA in your organization:
- Cost: Implementing MFA can get expensive as it involves certain hardware components as part of the solution, to carry out the various authentication techniques. Pick a solution that supports a variety of protocols, authenticators, and deployment options to ensure return on investment.
- User adoption and experience: Users initially tend to find the MFA process bothersome and time-consuming. It might hinder their productivity because of MFA fatigue. This is where adaptive MFA helps by pre-calculating the authenticity of users and reducing the number of MFA authenticators prompted for them.
- Authentication methods: It's important to support a variety of authenticators when you implement MFA. This ensures that users have an always-on alternative when they lose access to their their primary authentication method.
Implementing MFA with ADSelfService Plus
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus is an identity security solution ensuring secure access to enterprise resources and establishing a Zero Trust environment. It provides capabilities such as adaptive MFA, single sign-on, workforce self-service, and password management and security.
ADSelfService Plus offers different types of authentication techniques to enforce Active Directory MFA during:
- Machine logins (Windows, macOS, and Linux systems)
- RDP and VPN logins
- Enterprise application logins through SSO
- OWA logins
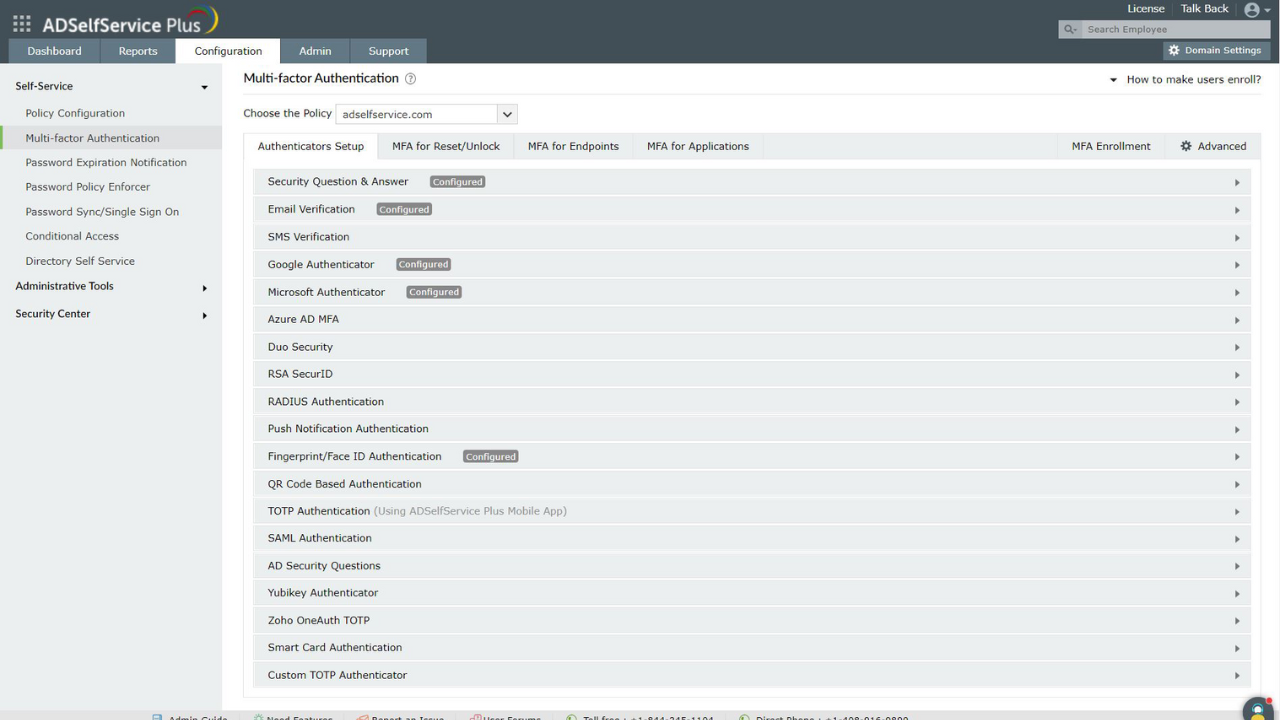
ADSelfService Plus offers 19 different authentication factors to secure user identities, as shown below.
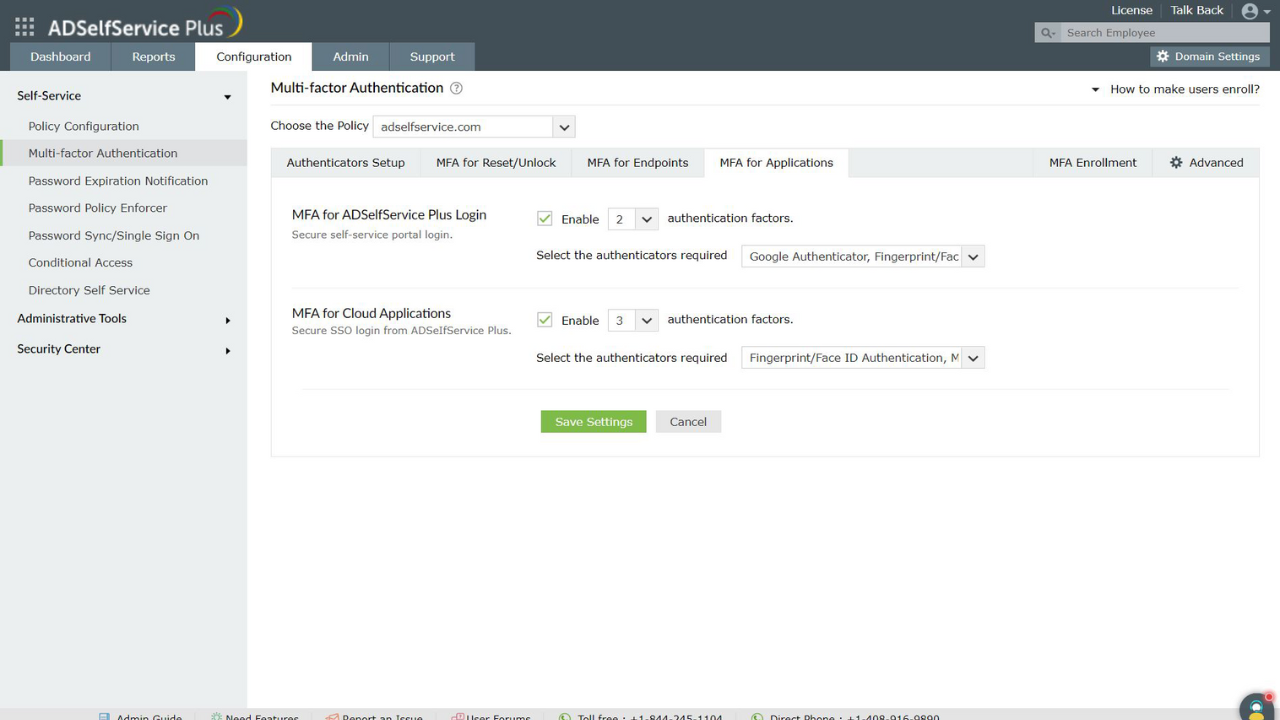
Implementing MFA with ADSelfService Plus also ensures that your organization complies with regulatory norms, like the PCI DSS, the GDPR, NIST 800-63B, SOX, and HIPAA.
To try out ADSelfService Plus for yourself, download a 30-day, free trial right away, or schedule a free, personalized web demo for a product expert to take you through ADSelfService Plus' identity security offerings.







Comments ( 0 )