Imagine a world where your data isn't vulnerable to misuse, hack, or exposure—that's like a utopia. That's where privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) step in, armed with sharp-edged tools and cunning ways to keep your private information safe.
From encrypting secrets to creating synthetic data doppelgängers, PETs ensure that your data stays yours in a world of big data and endless regulations. Like the bodyguards of the digital world, they help organisations and individuals remain in control.
In this article, we’ll explore privacy-enhancing technologies—what they are, why they matter, and how they’re changing how we protect our data.

What Are Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)?
PETs are innovative tools and methodologies designed to protect sensitive data and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of information. These technologies are essential for safeguarding personal data, even when information is shared for collaboration or advanced analytics.
Although data protection law does not explicitly define PETs, the concept encompasses a broad range of techniques and technologies aimed at addressing privacy risks.
The EU Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) describes PETs as software and hardware solutions that integrate technical processes, methods, or knowledge to deliver specific data protection or privacy functionalities.
PETs play a crucial role in various areas, including the secure training of AI models, generating anonymous statistics, and enabling data sharing between different organisations without compromising privacy.
Differential privacy, for example, creates anonymous statistics by randomising computations and introducing noise to outputs, ensuring sensitive data remains private.
Homomorphic encryption offers robust data security by allowing computations on encrypted data without requiring decryption. Trusted execution environments enhance security by isolating sensitive computations within a secure segment of a computer processor.
Federated learning enables the training of Machine Learning (ML) models across distributed systems while minimising the sharing of personal data between involved parties.
The significance of PETs lies in their alignment with data protection by design. They help organisations implement data minimisation principles effectively, ensuring only the data necessary for a specific purpose is processed.
These technologies provide robust solutions for anonymisation and pseudonymisation, minimising the risks of data breaches by rendering personal data unintelligible to unauthorised parties. Organisations that integrate PETs into their processes can demonstrate a data protection by default approach, complying with key GDPR requirements while reducing risks to individuals.
Adopting PETs enables organisations to balance data utility with privacy. These solutions are instrumental in facilitating advanced analytics and secure collaboration, ensuring compliance with data protection principles and maintaining trust with individuals whose data is being processed.
Types of PETs
Synthetic Data
Synthetic data enables organisations to generate artificial datasets that closely mimic real-world data while preserving privacy. Organisations can safeguard sensitive information by creating synthetic datasets while maintaining data utility for analysis and innovation.
These synthetic datasets replicate real data's shape and statistical qualities, ensuring accurate insights. For example, a well-designed synthetic dataset can maintain correlations, such as the relationship between age and heart disease, ensuring analysis remains robust and privacy intact.
Differential Privacy
Differential privacy is a mathematical framework that protects individual data by adding randomness or "noise" to query results. This method ensures that identifying specific data points becomes extremely difficult, enhancing privacy.
Not all noise-adding techniques meet the rigorous standards of differential privacy, making adherence to its principles crucial for secure data analysis.
Confidential Computing
Confidential computing revolutionises data security by enabling computations to occur within secure enclaves, protecting sensitive data even during active use. This cutting-edge technology prevents unauthorised access during data processing and analysis, setting a new benchmark for secure operations.
Key features of confidential computing include:
- Isolation: Protects data in use by securing it within a trusted execution environment.
- Remote attestation: Verifies that data remains secure and confirms its intended use before computations commence.
What Are the Risks of Using PETs?
PETs can play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, but they should not be regarded as a silver bullet for data protection. While PETs are designed to minimise privacy risks and help organisations meet compliance standards, they cannot address every potential vulnerability. Relying solely on these technologies may leave certain gaps in your data protection strategy.
One significant risk is the potential for misconfigured PETs, which can inadvertently expose sensitive information instead of protecting it. Additionally, over-reliance on PETs without integrating other robust data protection measures may weaken your overall security framework. Compatibility issues with existing systems can also arise, leading to operational inefficiencies and additional risks.
To maximise the effectiveness of PETs, organisations must adopt a holistic approach to data protection. This includes combining these technologies with best practices, continuous monitoring, and compliance strategies to ensure comprehensive protection.
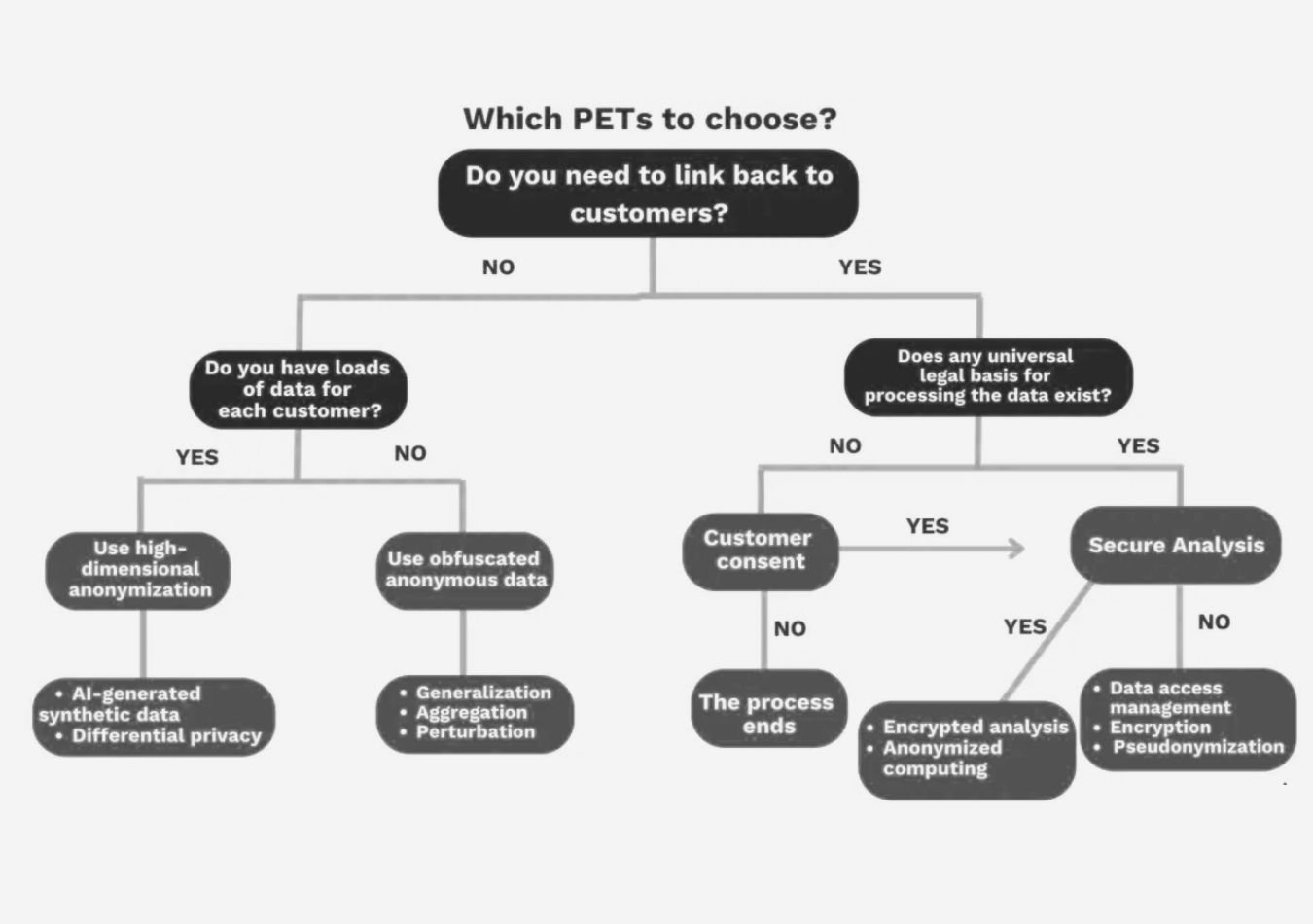
What Are the Benefits of Using PETs?
On the other hand, using PETs offers numerous benefits for businesses and individuals alike. These tools are designed to enhance data protection, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the GDPR.
By implementing PETs, organisations can:
- Strengthen data security – Safeguard sensitive information against breaches and unauthorised access.
- Enhance privacy compliance – Meet legal requirements for data privacy, avoiding costly penalties.
- Build customer trust – Demonstrate a commitment to protecting personal data, fostering loyalty and brand reputation.
- Enable data sharing with privacy protection – Collaborate securely without exposing sensitive details.
- Support ethical data use – Ensure responsible data handling while gaining insights through advanced analytics.
Integrating PETs into your operations can give your business a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world. By prioritising PETs, you protect your organisation and empower users with greater control over their information.






Comments ( 0 )