While it may now be one of the world’s biggest smartphone sellers, no tech company has stirred up quite as much controversy as Huawei.
The Chinese conglomerate, a global leader in cutting-edge 5G technology and smartphones, continues to rattle Western governments and lawmakers as its influence in the telecoms industry intensifies.
Most recently, the firm has faced allegations, primarily from the United States and its allies, that its wireless networking equipment could contain backdoors enabling surveillance by the Chinese government.
These concerns have intensified with Huawei's involvement in the development of 5G wireless networks, and have led to some countries implementing or contemplating restrictions on the use of Chinese-made hardware in these networks.

But what really is the problem with Huawei? And why have so many Western governments banned Huawei technology from their countries? For that, we’ll need to start from the beginning.
This article delves deep into the Huawei controversy, exploring the various events that led to the company being banned in the US and other Western countries.
What is Huawei?
Huawei is a Chinese multinational technology company headquartered in Shenzhen. Founded in 1987, Huawei has rapidly grown to become one of the world's largest providers of 5G networks, telecommunications equipment and consumer electronics.
Known for its innovative products and competitive pricing, Huawei has gained a significant market share in various sectors, including smartphones, networking equipment, and cloud computing.
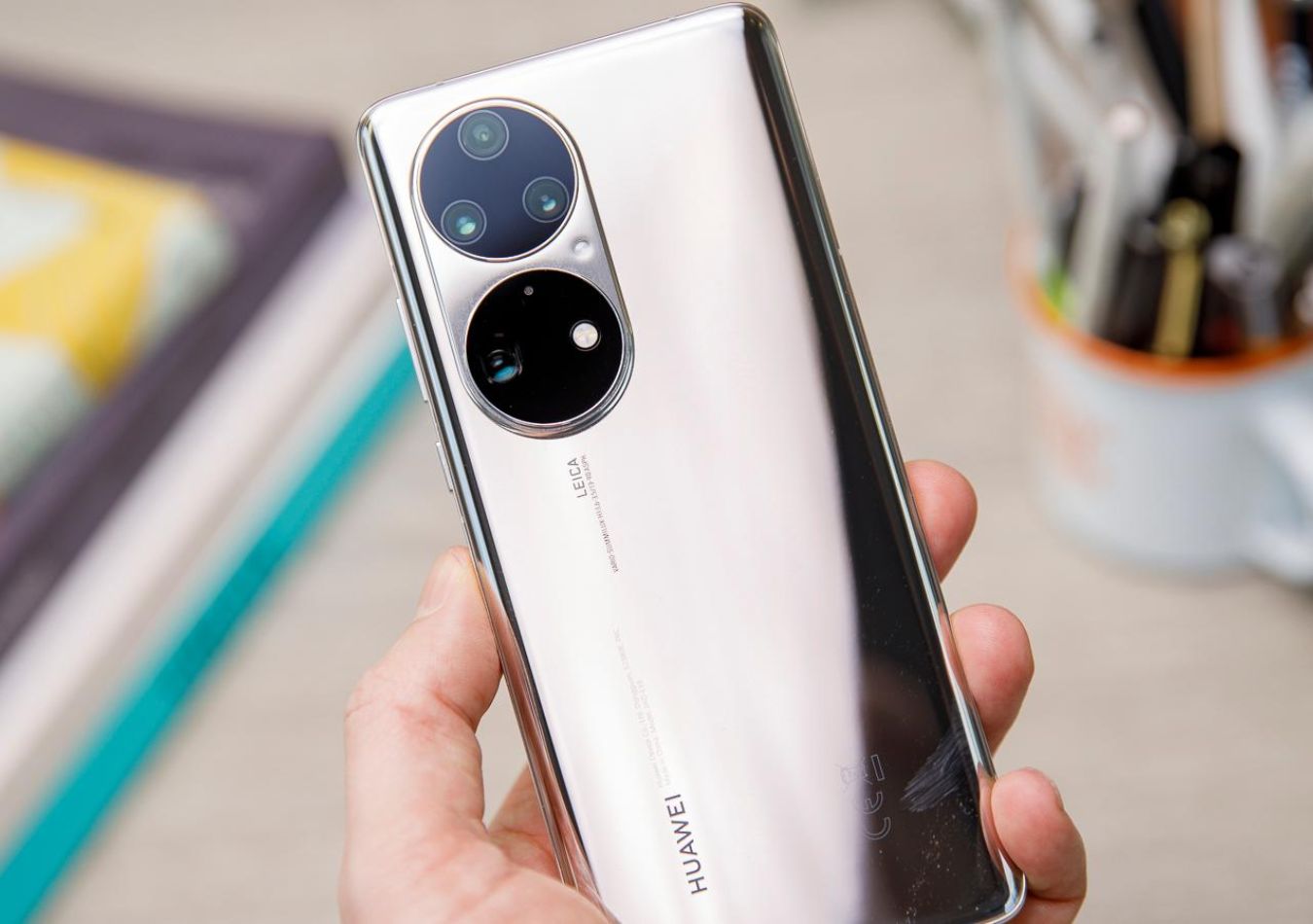

The company's flagship smartphones, such as the Mate and P series, have garnered widespread recognition for their advanced features and high-quality performance, helping the firm take over Samsung in 2021 to become the largest smartphone maker in the world.
However, Huawei has also faced intense scrutiny in recent years. The company has been subject to intense scrutiny from Western governments over concerns about its potential ties to the Chinese government and its alleged national security risks.
In response, Washington and its allies have imposed sweeping restrictions on Huawei as part of a larger crackdown on Chinese technology companies.

Inside Neuralink’s Human Trial
First-in-human brain implant shifts BCIs from lab concept to live deployment, raising new questions on regulation, access and clinical benefit.
When did the controversy with Huawei begin?
The controversy surrounding Huawei escalated in the 2000s when US officials within the federal government began raising concerns that Huawei-made telecom equipment may be designed to allow unauthorised access by the Chinese People's Liberation Army.
The main reason for this concern was that Huawei founder Ren Zhengfei served as an engineer in the army in the early 1980s.
The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States also scrutinised a deal by Bain Capital to acquire 3Com with Huawei as a minority investor, and an attempt to acquire the virtualization firm 3Leaf Systems, both due to security concerns (with concerns that China could gain access to U.S. military-grade technology in the case of the former).
However, it wasn’t just security concerns that sparked controversy with Huawei. Throughout the 2000s, US companies and global telecom firms have for years accused Huawei of stealing trade secrets.
This began with Cisco’s 2003 lawsuit alleging that its source code appeared in Huawei products. By July 2004, Huawei removed the contested code, manuals and command-line interfaces and the case was subsequently settled out of court. As part of the settlement, Huawei admitted that it had copied some of Cisco's router software.

Then in 2017, a U.S. jury found Huawei guilty of stealing intellectual property from the US telecoms company T-Mobile, and in 2020, the U.S. Justice Department charged Huawei with racketeering conspiracy and conspiracy to steal trade secrets.
According to the indictment, these violations allowed Huawei to “drastically cut its research and development costs and associated delays, giving the company a significant and unfair competitive advantage.”
When Training Data Breaks IP
Record labels challenge how AI music models are trained, spotlighting data sourcing, consent, and fair use as core infrastructure risks.

A list of notable Huawei controversies
1. Intellectual Property Theft Allegations (2003)
In 2003, Cisco Systems accused Huawei of stealing its intellectual property. Cisco claimed that Huawei had copied its source code and other proprietary information. Huawei denied these allegations, but the dispute led to a lawsuit in the United States. While the case was eventually settled out of court, the allegations damaged Huawei's reputation and raised questions about its ethical business practices.
2 . U.S. House Intelligence Committee Concerns (2012)
In 2012, the U.S. House Intelligence Committee released a report expressing concerns about the potential security risks posed by Huawei and ZTE. The report suggested that these companies could be used by the Chinese government for espionage or sabotage. The committee recommended that U.S. companies avoid doing business with Huawei and ZTE, citing the potential threat to national security.
3. U.S. Department of Justice Investigation (2016)
In 2016, the U.S. Department of Justice opened a criminal investigation into Huawei for allegedly violating U.S. sanctions against Iran. The department accused Huawei of deceiving U.S. banks about its business dealings with Iran. This investigation intensified concerns about Huawei's compliance with U.S. laws and regulations.

Right to Repair vs Design Limits
Examine the clash between repair legislation and product strategies built on short lifecycles, margin protection, and upgrade churn.
4. Global Ban on Huawei 5G Equipment (2018-2019)
In 2018, the U.S. government began a campaign to pressure its allies to ban Huawei from their 5G networks. The U.S. argued that Huawei's equipment could be used by the Chinese government for surveillance or espionage. In response, several countries, including the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand, announced bans on Huawei equipment in their 5G networks.
6. Arrest of Meng Wanzhou (2018-2021)
In 2018, Huawei's CFO, Meng Wanzhou, was arrested in Canada at the request of the United States. The U.S. accused Meng of deceiving banks about Huawei's business dealings with Iran. Meng spent nearly three years under house arrest in Canada before being released in September 2021. Her arrest sparked a diplomatic crisis between China and the United States.
5. Entity List and Further Sanctions (2019-2021)
In 2019, the U.S. Department of Commerce added Huawei to the Entity List, restricting U.S. companies from doing business with it without a license. This move severely impacted Huawei's operations, as it relied on U.S. technology to manufacture its products. In 2020, the U.S. government imposed further sanctions on Huawei, limiting its access to essential technologies. These sanctions have made it difficult for Huawei to compete in the global market.
Europe Rewrites AI Rules
Italy’s ChatGPT ban signals a new regulatory playbook for generative AI, with GDPR enforcement shaping global deployment strategies.

Is Huawei banned?
Huawei is banned from many Western countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and Canada. These countries have imposed restrictions on Huawei's operations due to concerns about its potential security risks, including the possibility of its equipment being used for surveillance or espionage by the Chinese government.
The United States Department of Commerce added Huawei to the Entity List in 2019, restricting U.S. companies from doing business with it without a license. This move severely impacted Huawei's operations, as it relied on U.S. technology to manufacture its products.
In addition to the U.S. ban, several other countries have also restricted Huawei's operations. The United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand have banned Huawei equipment from their 5G networks, citing concerns about national security. These bans have significantly limited Huawei's access to important markets and hindered its growth.
While Huawei has challenged these bans and restrictions, it has faced significant obstacles in overcoming them. The company has had to adapt its business model and seek alternative suppliers to continue its operations. However, the ongoing restrictions have put Huawei at a competitive disadvantage and have raised questions about its long-term viability.
Why was Huawei banned in the US?
The main reason for the US ban on Huawei is that its equipment could be used for surveillance or espionage by the Chinese government. This fear was fueled by Huawei's close ties to China, its founder's military background, and the potential for Chinese government control.
The US government argued that Huawei could pose a risk to national security since – as is the case with TikTok – it could be forced by the China government to spy on critical US infrastructure, intercept communications, or steal sensitive data upon request. These concerns led to the US sanctioning Huawei and eventually banning its operations in the United States.
Along with security concerns, there have been allegations that Huawei may have violated US sanctions against Iran and North Korea, fueling concerns about Huawei's compliance with international laws and regulations.

These sanctions violations, paired with the firm’s security risks, led Western countries, including the United States, Australia, and the United Kingdom, to impose bans on Huawei equipment in their 5G networks.
These bans were intended to protect the security and integrity of Western countries' telecommunications networks to mitigate the potential risks associated with the company's controversies However, they have also faced significant criticism.
Some argue that the bans are based on unfounded fears and could harm global technological innovation. Others maintain that the potential security risks posed by Huawei are too great to ignore.






Comments ( 0 )