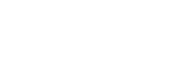What is Character AI and is it Safe to Use?
AWS vs Azure: What’s the Difference in 2024?

Becoming a modern organization today means adopting cloud computing in some capacity.
94% of all companies globally used some kind of cloud computing service in 2023, and that number is only set to increase with the increasing adoption of workload-hungry technologies like AI and edge computing as we head into 2024.
With the cloud increasingly becoming the new norm for organizations big and small, you’d think many organizations would have their fingers on the pulse of the big players on the market.
But with the increasing prevalence of multi-cloud – where multiple cloud providers are used at the same time – many have no idea how some of the key cloud service providers work and when they should be used.
In this article, we’re going to be looking at two of the biggest cloud service providers available today – Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
We’ll be comparing the key differences between AWS vs Azure, as well as exploring the benefits of using each of them and the scenarios when each of them should be used.
What is AWS?
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a cloud computing platform offered by Amazon that provides various on-demand services like storage, compute power, databases, and more.
AWS offers a huge range of services – over 200, in fact – that let you do things like store data online, run websites and applications, or process information. Instead of having your own physical servers or computers, you can access AWS's servers on-demand over the Internet.

Traditionally, businesses would have their own physical servers and data centres to run their applications. This requires a lot of upfront cost and maintenance. With AWS, businesses rent virtual servers and other resources in the cloud. This gives you the flexibility to scale your resources up or down depending on your needs and Pay only for what you use.
What is AWS used for?
One of the most common uses of AWS is to store and run websites and applications. AWS offers virtual servers, databases, and other tools that make it easy to develop and deploy web applications on the cloud, as well as tools and services specifically designed to aid in developing and deploying mobile applications.
Businesses can also use AWS to store large amounts of data online, securely and reliably. This can be used for things like backing up important files, storing customer data, or hosting large media files.
AWS offers a variety of services that can be used for data analytics and machine learning too, allowing businesses to gain insights from their data and develop intelligent applications to help them manage it.
Businesses requiring complex calculations can also utilize AWS's high-performance computing resources for tasks like scientific simulations, financial modelling, video rendering, and many more.
What are the most popular AWS services?
1. Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
S3 is the go-to cloud storage service AWS. It provides highly scalable, durable, and cost-effective object storage for a massive range of data. Think of it as a giant online hard drive accessible from anywhere. People use S3 for things like:
- Storing application data and backups
- Hosting websites with static content (images, videos, etc.)
- Data lakes for big data analytics
2. Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
This service offers virtual servers in the cloud, similar to renting computing power instead of buying physical servers. EC2 provides a wide range of server configurations (CPU, memory, storage) to suit various application needs. It's popular for:
- Running web applications
- Hosting development and testing environments
- Deploying high-performance computing clusters
3. Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
RDS simplifies managing databases by providing a managed relational database service for popular database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Aurora. It handles tasks like provisioning, patching, and backups, freeing you to focus on your application. Developers use RDS for:
- Running database-backed web applications
- Storing and managing customer data
- Building data-driven applications
4. AWS Lambda
Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your code and AWS takes care of everything else, making it ideal for event-driven applications or microservices that only need to run when triggered by an event. Common uses include:
- Processing data streams from sensors or IoT devices
- Responding to user actions on a website or application
- Automating tasks triggered by events (e.g., resizing images on upload)
5. Amazon CloudFront
CloudFront is AWS's content delivery network (CDN). It distributes content globally with high performance and security. By caching content at geographically dispersed locations, CloudFront reduces load times for users worldwide. This is a go-to service for:
- Delivering static content for websites and applications
- Streaming media content
- Improving website performance for global audiences
What is Azure?
Microsoft Azure, often shortened to just Azure, is another popular cloud computing platform created by Microsoft. Like AWS, It's not just a product, but a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a vast array of services to businesses and developers of all sizes.
With Azure, instead of relying on physical servers and infrastructure housed on-site, your resources reside in Microsoft's secure data centers around the globe.

You then access Azure services through the internet, using a web browser or specialized tools, and Azure provides a pay-as-you-go model, so you only pay for the resources you use. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and software, offering a pay-as-you-go model that is easier on the budget.
Azure seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products like Office 365 and Dynamics 365, as well as many third-party tools, providing a unified experience and simplifying workflows.
What is Azure used for?
Azure acts as a virtual storehouse for a vast range of cloud computing services, which can broadly be categorized into three main areas: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)
IaaS removes the need for physical servers, and you essentially rent virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking resources. Need a powerful VM for a complex simulation? Azure provides it. Don't require all that horsepower during off-peak hours? You can easily scale down and save costs.
With PaaS, Azure provides a platform for you to develop, deploy, and manage your applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It is a complete platform for building and deploying applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Programming languages, development tools, databases – Azure provides a pre-configured environment, allowing developers to focus on crafting exceptional applications.
With SaaS, you can access pre-built software applications directly through Azure, eliminating the need for installation on your own devices. This caters to users who need ready-made applications. Don't want the hassle of installing software or managing licenses? With SaaS, applications are delivered directly through Azure, accessible from any device with an internet connection.
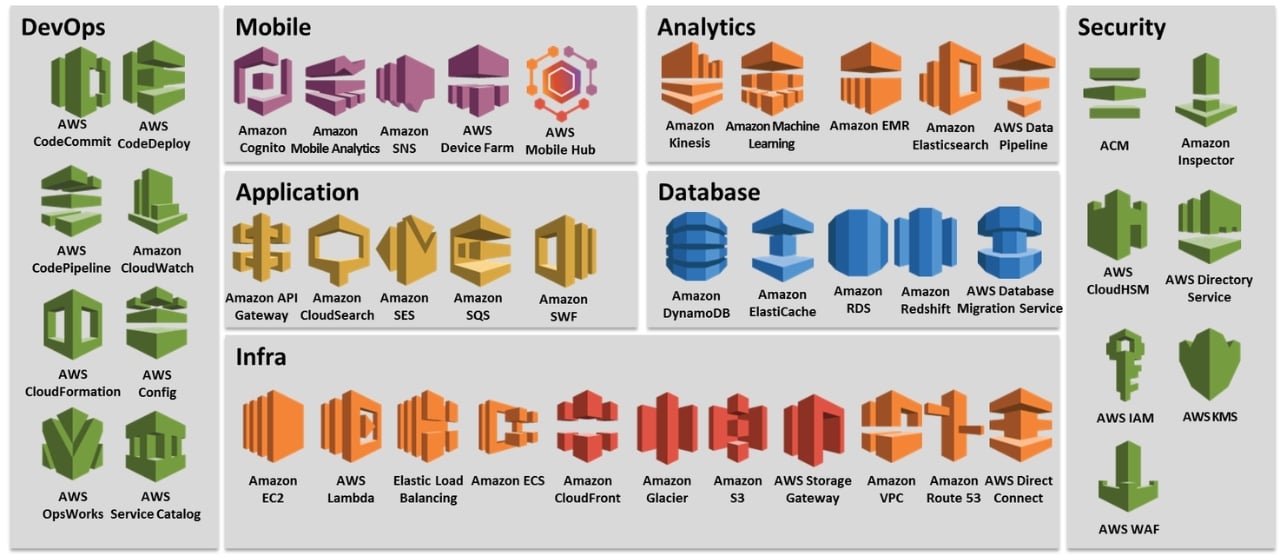
What are the most Common AWS services?
1. Azure Virtual Machines (VMs)
Azure VMs allow you to rent virtual machines with different configurations of CPU, memory, and storage. It provides the flexibility of a traditional on-premises data center but with the scalability and cost-efficiency of the cloud.
2. Azure App Service
This service streamlines building and deploying web applications (mobile or web) without managing servers. It supports various programming languages and frameworks, making it a popular choice for developers.
3. Azure Functions
This serverless compute service lets you run code without managing servers. You simply write code snippets triggered by events (like a database change) and Azure takes care of the rest.
4. Azure Cosmos DB
This globally distributed database service offers high availability, scalability, and consistency for your data. It's perfect for mission-critical applications requiring low latency and global reach.
5. Azure Resource Manager (ARM)
This service simplifies managing and deploying your Azure resources. It allows you to define infrastructure as code, enabling automation and consistency in your deployments.
AWS vs Azure: What’s the difference?
AWS and Azure are the two biggest players in the cloud computing market, but AWS currently holds the lead with a 33% market share compared to Azure’s 23% share and boasts a much wider range of services to cater to this larger audience.
Azure, however, excels in its integration with Microsoft products and services, making it the ideal choice for businesses heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. It’s also growing and quickly catching up to AWS, and many users find Azure easier to use thanks to its more fine-tuned approach and user-friendly interface.
Of course, there are many other differences between Azure and AWS. To understand which cloud platform is better for you, it’s important to think about what you’re using them for.
Let’s run through some of the pros and cons of using AWS vs Azure:
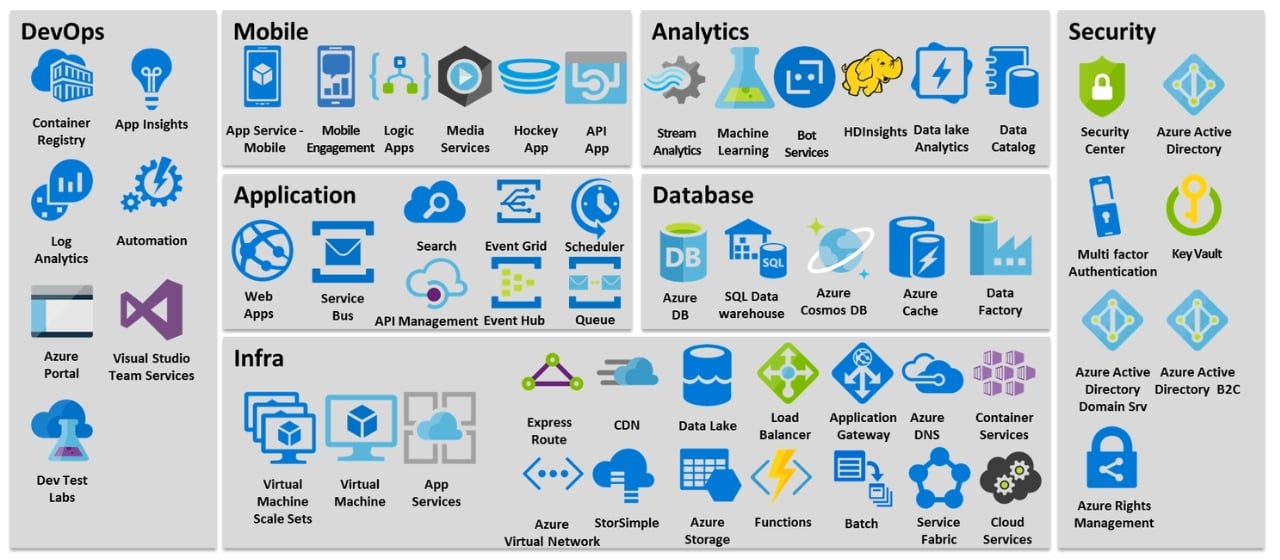
Key Differences
Market Share and Maturity
Launched in 2006, AWS is the current leader with a dominant market share (around 33%) and a longer track record, offering a wider range of services. Azure holds the second position at around 23%, and launched in 2010 is quickly catching up to AWS.
Due to its larger market share and longer history, AWS has a more established reputation and a wider variety of services that have been around for a longer time. This can be advantageous if you need a very specific service or prioritize stability.
While not quite as dominant in market share, Azure is growing rapidly and excels in specific areas like integration with Microsoft products. Its relative youth can also be a benefit, as its services may be built with newer technologies and user experiences in mind.
Features
AWS is known for its extensive range of services, strong Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offerings, and well-established APIs. Azure, however, shines in Platform as a Service (PaaS) solutions, tight integration with Microsoft products and developer tools.
Both AWS and Azure boast a global network of data centres, meaning your applications are accessible from anywhere in the world no matter which you opt for.
Pricing
Azure is generally considered more cost-effective than AWS, especially for Windows Server and SQL Server workloads due to potential integration benefits with existing Microsoft licenses. Azure can also be much more straightforward in pricing, especially for existing Microsoft license holders and Windows workloads.
However, pricing structures can be complex and depend on the specific service you’re using, so AWS can be more cost-effective with proper cloud-cost optimization.
Security
Security is a top priority of AWS and Azure, and both cloud platforms have reliable security features and compliance certifications to keep your data safe.
Ease of Use
AWS can have a steeper learning curve than Azure due to its more complex interface, and navigating the sheer number of options can be overwhelming for beginners. Azure, on the other hand, is generally considered more user-friendly, especially for those familiar with Microsoft products.
If you're new to cloud computing entirely, both platforms will require some learning. However, AWS might demand more initial effort to grasp its functionalities. Those with some experience in Microsoft products will also likely find Azure's interface more intuitive. Existing knowledge of services like Office 365 can translate well to using Azure.
Should you choose AWS or Azure?
Ultimately, the best platform depends on your specific requirements. Consider your existing infrastructure, budget, technical expertise, and the types of services you need most.
Still, AWS might be a better fit if you need a very specific or niche service not offered by Azure, you already have a significant investment in AWS services or your priorities lie in a broad range of IaaS options.
A zure, however, is probably the better choice if you heavily rely on Microsoft products and services for your workflow, need a user-friendly interface and strong developer tools or our primary needs lie in PaaS solutions.